This is part four in a series of posts exploring Istio, a popular service mesh available for Kubernetes. In this post, I’ll look at what a ServiceEntry resource is and where it fits in this stack.
- The Sample application.
- The VirtualService resource.
- The DestinationRule resource.
- The ServiceEntry resource.
- The Gateway resource.
In order to make a network request, the destination host must be part of the Istio service registry. By default, any Service resource in a Kubernetes cluster is part of the service registry, but external URLs are not. To expose external network applications to Istio, we use the ServiceEntry resource.
In this post, we’ll add a ServiceEntry resource to the Kubernetes cluster in order to direct our proxy application to an external resource.
Redirecting internal requests to external resources
To demonstrate the ServiceEntry resource, we’ll direct the requests to http://webserver from the proxy to https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mcasperson/NodejsProxy/master/externalservice1.txt. This is a plain text file containing the text External Service 1 that is hosted by GitHub. We’re using this text file to simulate an external API endpoint.
The first step is to expose the host raw.githubusercontent.com to the Istio service registry, which is achieved with a ServiceEntry resource.
In the YAML below we expose the host raw.githubusercontent.com, identified as being external to the Istio mesh via the MESH_EXTERNAL property, accepting HTTPS traffic on the standard port of 443, and resolved to an IP address using the DNS server available inside the Kubernetes cluster with the DNS property:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: github
spec:
hosts:
- "raw.githubusercontent.com"
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 443
name: https
protocol: TLS
resolution: DNSWith the external service now part of the Istio service registry, we need to direct traffic to it. This is achieved with the VirtualService resource.
As before, we are matching requests to the webserver host and using the rewriting functionality to route the request to another location. However, unlike the previous blogs, we are rewriting the traffic to point to an external location.
It is important to set the authority to the same value as the destination.host, because a large number of external services expect the HOST header in the HTTP request to be defined correctly. Failure to set the authority field can lead to odd 404 errors.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: webserver
spec:
hosts:
- webserver
http:
- match:
- uri:
regex: ".*"
rewrite:
uri: "/mcasperson/NodejsProxy/master/externalservice1.txt"
authority: raw.githubusercontent.com
route:
- destination:
host: raw.githubusercontent.com
port:
number: 443Because we have redirected a HTTP call to an internal Service resource to a HTTPS external location, we need to configure a DestinationRule resource to act as a TLS client. In the YAML below, we have configured the DestinationRule resource to SIMPLE TLS mode, which indicates that requests to the host should be conducted over a TLS connection:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: github
spec:
host: "raw.githubusercontent.com"
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: SIMPLEWith this combination of ServiceEntry, VirtualService, and DestinationRule resources, we have pointed our proxy application out to the text file hosted by GitHub:
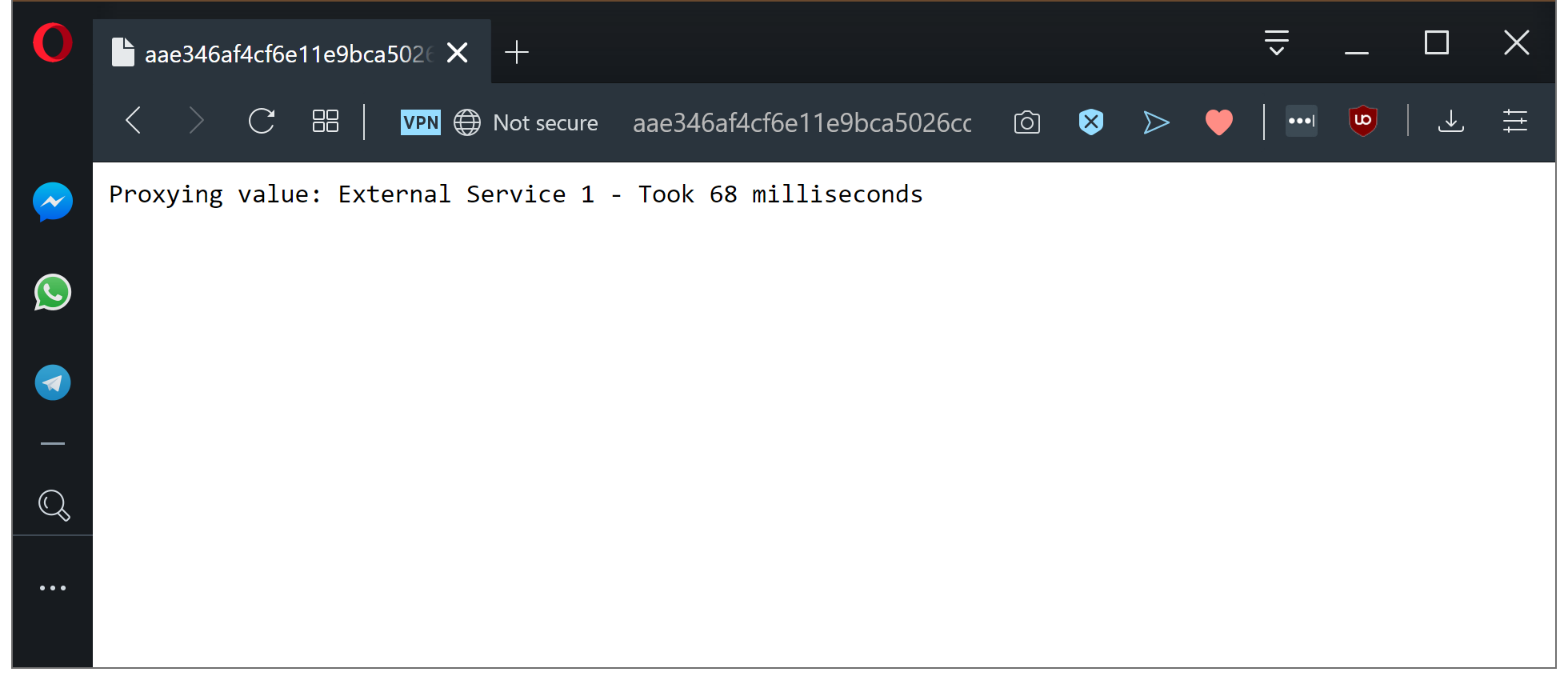
Internal requests are now directed to an external host.
Here is the architecture diagram showing the ExternalService resource and the new flow of requests to the external resources.
The architecture diagram with the ServiceEntry resource (in purple).
Conclusion
Istio requires that any external resources contacted by internal applications be exposed as part of the service registry. In this post, we exposed a text file hosted by GitHub via a ServiceEntry resource, directed traffic to it via a VirtualService resource, and configured the TLS settings required to access the HTTPS site via a DestinationRule resource. The end result is that our sample application made requests to the external location without having to modify any code.
In the next post we will look at the Gateway resource, and how it is used to direct external traffic into the cluster.