In line with our public roadmap, we introduced built-in support for Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
With this addition, Octopus now offers built-in support for the three major cloud providers:
This meets the evolving needs of our customers, particularly those who have GCP Kubernetes clusters and are running Tentacles on GCP virtual machines.
Built-in integration of Octopus with GCP allows you to:
- Connect and authenticate with GCP via a dedicated account type - this allows you to centralize and secure your GCP authentication and use it in your deployments and runbooks
- Use gcloud, the GCP command-line tool, in custom scripts out-of-the-box
- Create and tear down GCP infrastructure with Terraform
- Access Docker images hosted with Google Container Registry (GCR)
- Deploy, scale and manage containerized applications on GCP with Octopus and Kubernetes
GCP integration is available in Octopus Deploy 2021.2 and newer. Octopus Cloud customers are already running this version, and on-premises customers can download it now.
Learn more about the Octopus 2021.2 (Q3) release in our release announcement.
How to deploy to Google Cloud
To see this new integration in action, this post explains how to add a new Google Cloud account in Octopus, and run a gcloud script to create a new Kubernetes cluster.
Google Cloud accounts
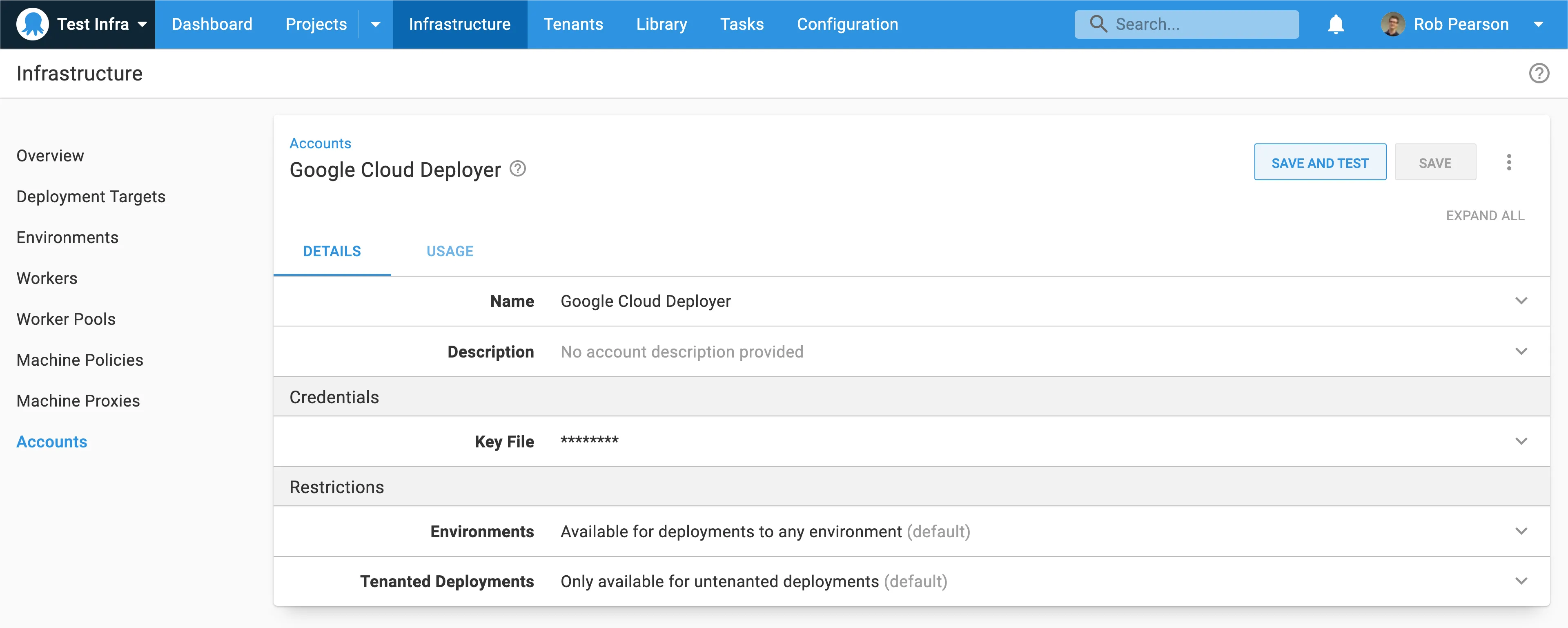
To integrate with GCP, first define a Google Cloud account in Octopus. Do this in {{Infrastructure > Accounts}}, alongside any AWS or Azure accounts you already have.
Octopus manages the GCP credentials used by the Google Cloud steps. This means you don’t need to worry about authentication in a deployment process or runbook, and you can run pre-authenticated gcloud scripts.
Google Cloud accounts are secured by the JSON credentials key file, which can be retrieved from the service account assigned to the instance that is executing the deployment.
Learn more about creating a Google Cloud account and see the Google Cloud documentation for instructions on creating a service account and downloading the key file.
Google Cloud account variable
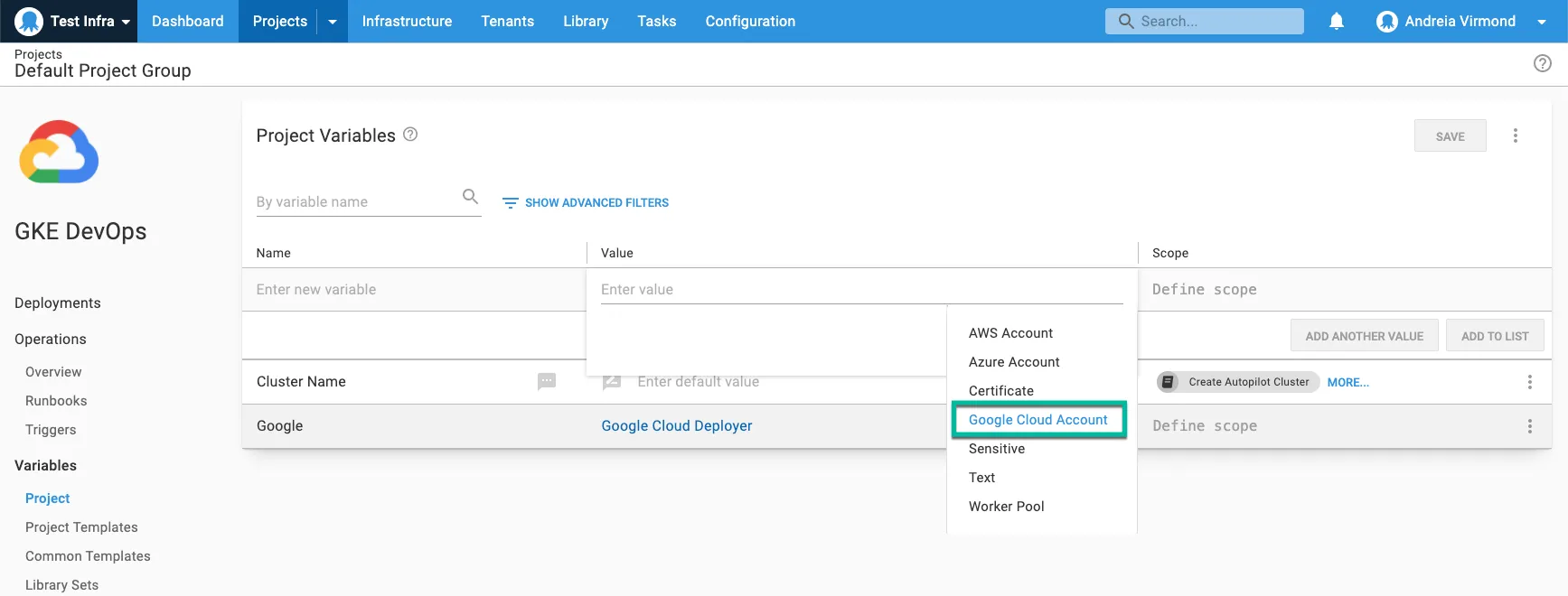
After you create Google Cloud accounts, they can be accessed in a project through a project variable of the type Google Cloud Account. Project variables are available to both deployment and runbook processes.
Learn more about setting up Google Cloud account variables in our docs.
Running gcloud scripts
Octopus Deploy helps you run scripts on targets with the Google Cloud Platform. In this example, we create a new Kubernetes cluster.
These scripts typically rely on tools being available on the target Workers, however there are a few options to get started quickly:
- If you’re using Octopus Cloud, the built-in “Windows 2016” Dynamic Workers have
gcloudpre-installed. - Another option is using the Octopus
worker-toolsDocker image with execution containers for workers. - In general, we recommend provisioning your own tools on your Worker. This gives you control over tool versions, and can ensure their compatibility with the scripts you’re trying to execute.
Workers move deployment work off the Octopus Server and onto other machines running in Worker Pools. Octopus Cloud uses them to execute custom scripts and they’re also commonly used to run deployment and runbook work for cloud platforms and database deployments.
Read our documentation about Workers and Worker Pools to learn more.
When executing a script against GCP, Octopus automatically uses your provided Google Cloud account details to authenticate you to the target instance. Alternatively, you can use the service account associated with the target instance.
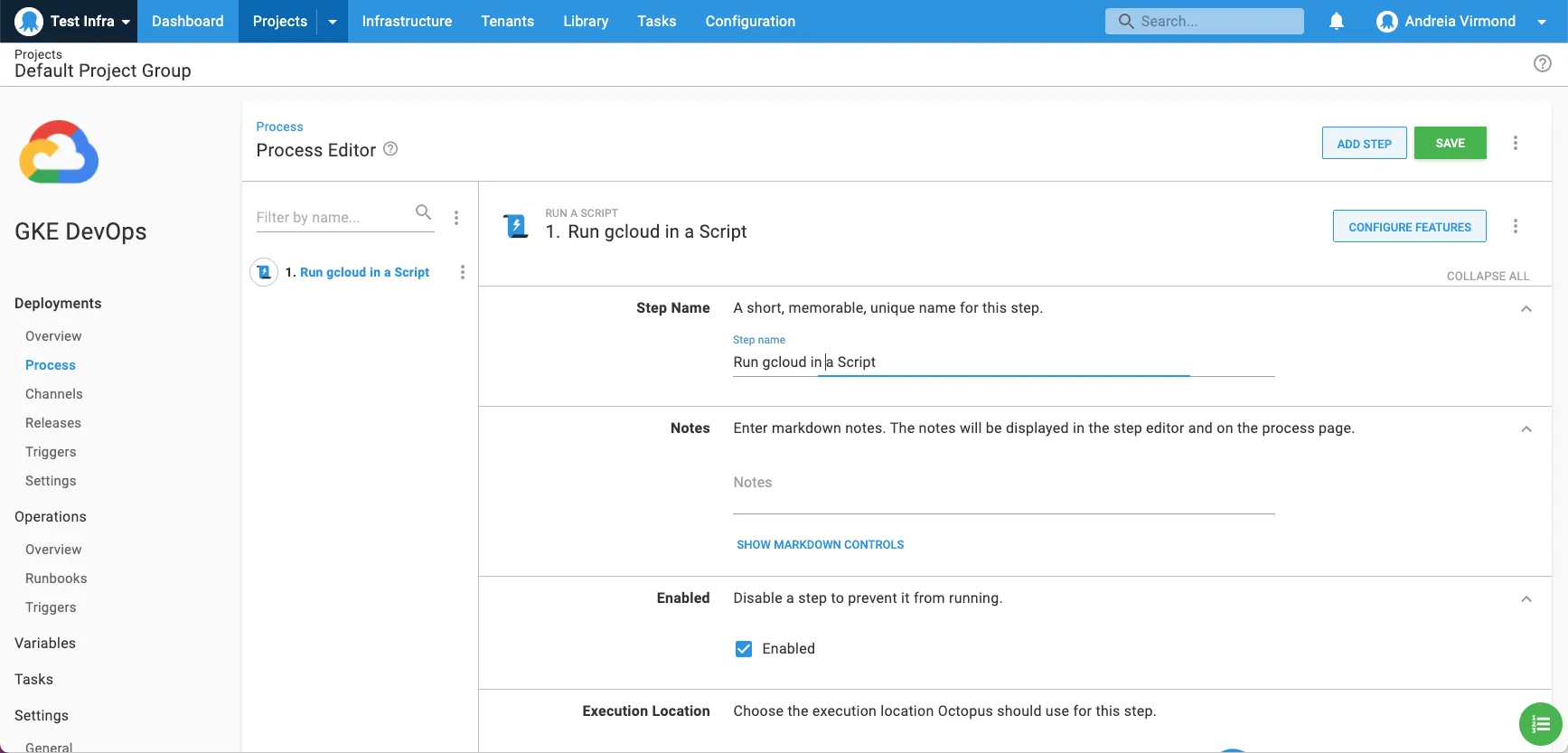
In this example, you add a new runbook process to create a new Kubernetes cluster using the gcloud command-line interface.
To do this, add a Run gcloud in a Script step to your automated process with a gcloud container clusters create command.
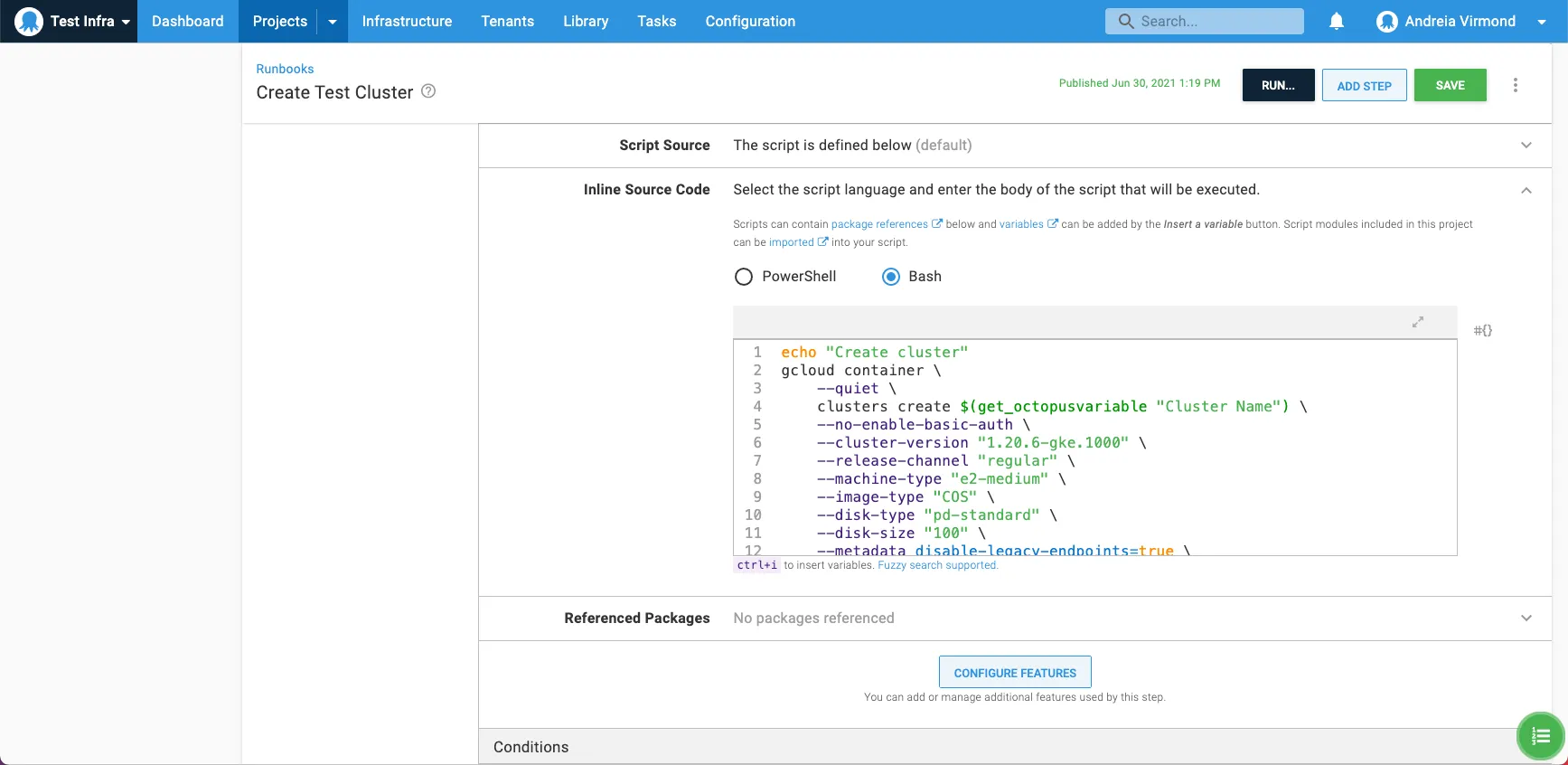
You need to customize the script for your needs, but it should look something like this:
echo "Create cluster"
gcloud container \
--quiet \
clusters create $(get_octopusvariable "Cluster Name") \
--no-enable-basic-auth \
--cluster-version "1.20.6-gke.1000" \
--release-channel "regular" \
--machine-type "e2-medium" \
--image-type "COS" \
--disk-type "pd-standard" \
--disk-size "100" \
--metadata disable-legacy-endpoints=true \
--scopes "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only","https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write","https://www.googleapis.com/auth/monitoring","https://www.googleapis.com/auth/servicecontrol","https://www.googleapis.com/auth/service.management.readonly","https://www.googleapis.com/auth/trace.append" \
--num-nodes "3" \
--enable-stackdriver-kubernetes \
--enable-ip-alias \
--network "projects/<your project>/global/networks/default" \
--subnetwork "projects/<your project>/regions/australia-southeast1/subnetworks/default" \
--default-max-pods-per-node "110" \
--no-enable-master-authorized-networks \
--addons HorizontalPodAutoscaling,HttpLoadBalancing,GcePersistentDiskCsiDriver \
--enable-autoupgrade \
--enable-autorepair \
--max-surge-upgrade 1 \
--max-unavailable-upgrade 0 \
--enable-shielded-nodesConclusion
We hope you enjoy deploying infrastructure to Google Cloud Platform.
Try it and let us know what you think. If you have any questions or comments, we’d love to hear them. Please use the comments section below or join the conversation in the Octopus community Slack.
Happy deployments!
Related posts

Improved control over package retention
Optimize efficiency with our latest package retention enhancements
Help shape Ephemeral Environments
Learn about Ephemeral Environments, coming soon to Octopus, and help us shape the feature.

New to our Enterprise tier
Octopus 2025.2 includes new features for our Enterprise tier.