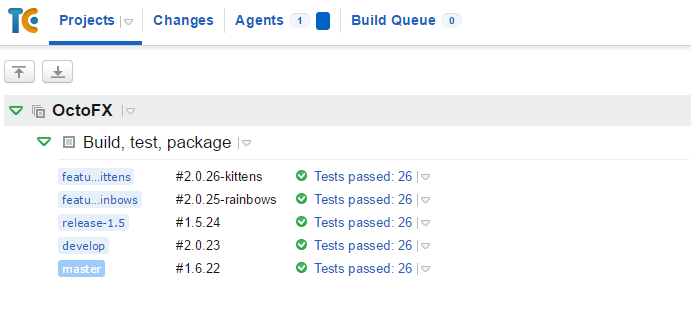
When you use TeamCity to build a project with multiple branches, it’s desirable to have different build numbers depending on the branch. For example, instead of simple TeamCity build numbers like 15, 16, and so on, you might have:
- Branch
master:1.6.15. - Branch
release-1.5:1.5.15(major/minor build from branch name). - Branch
develop:2.0.15(different minor build). - Branch
feature-rainbows:2.0.15-rainbows(feature branch as a tag).
Here’s how it looks:
Handling a branching workflow like GitFlow, and using these version formats, turns out to be pretty easy with TeamCity, and in this blog post I’ll show you how. Your own versioning strategy is likely to be different, but hopefully this post will get you started.
Background
First, there are two built-in TeamCity parameters that we care about:
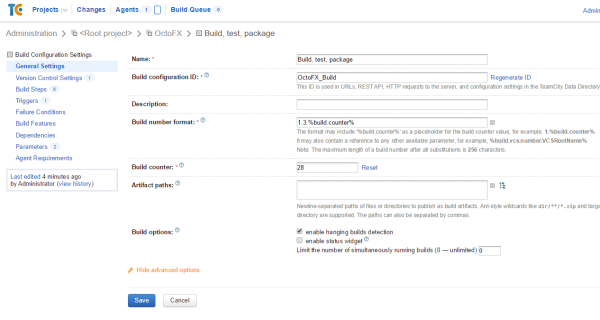
build.counter: this is the auto-incrementing build counter (15 and 16 above).build.number: this is the full build number. By default, it is%build.counter%, but it can be more complicated.
The format of build.number and value of build.counter is defined in the TeamCity UI:
However, you can also set it dynamically during the build, using service messages. That is, your build script can write the following text to stdout:
##teamcity[buildNumber '1.1.15']
This will override the build number, and the new value will then be passed to the rest of the steps in the build.
Putting it together
Depending on whether the branch name is master or develop, we will use different major/minor build numbers. To do this, we’re going to define two parameters in TeamCity. These need to be system parameters in TeamCity so that they can build scripts.
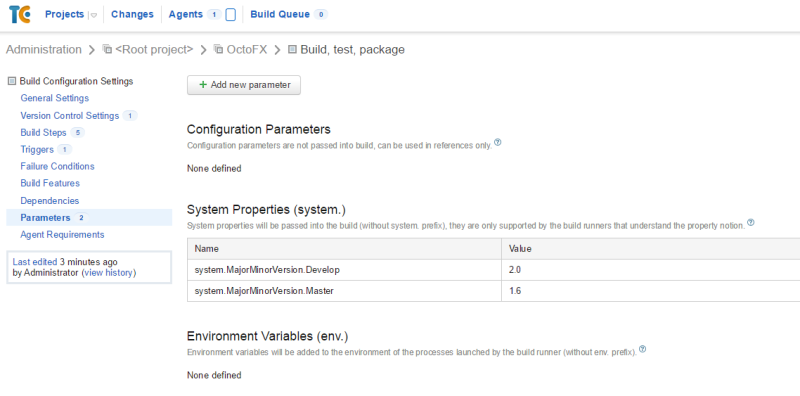
To dynamically set the build number based on the branch name, I’m going to add a PowerShell script step as the first build step in my build:
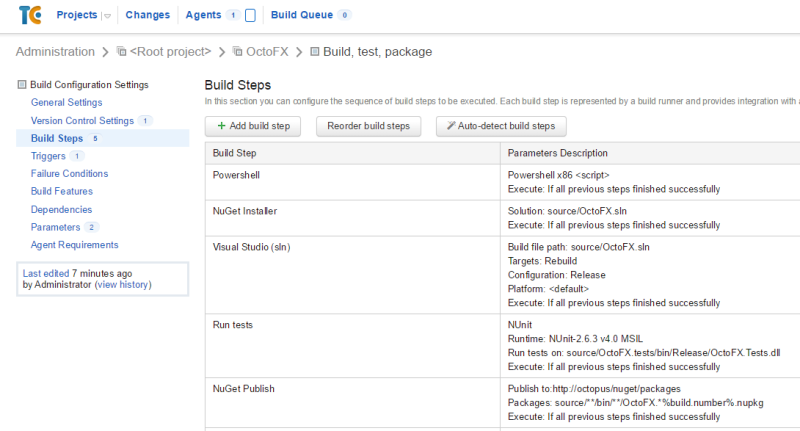
Finally, here’s the PowerShell script:
# These are project build parameters in TeamCity
# Depending on the branch, we will use different major/minor versions
$majorMinorVersionMaster = "%system.MajorMinorVersion.Master%"
$majorMinorVersionDevelop = "%system.MajorMinorVersion.Develop%"
# TeamCity's auto-incrementing build counter; ensures each build is unique
$buildCounter = "%build.counter%"
# This gets the name of the current Git branch.
$branch = "%teamcity.build.branch%"
# Sometimes the branch will be a full path, e.g., 'refs/heads/master'.
# If so we'll base our logic just on the last part.
if ($branch.Contains("/"))
{
$branch = $branch.substring($branch.lastIndexOf("/")).trim("/")
}
Write-Host "Branch: $branch"
if ($branch -eq "master")
{
$buildNumber = "${majorMinorVersionMaster}.${buildCounter}"
}
elseif ($branch -eq "develop")
{
$buildNumber = "${majorMinorVersionDevelop}.${buildCounter}"
}
elseif ($branch -match "release-.*")
{
$specificRelease = ($branch -replace 'release-(.*)','$1')
$buildNumber = "${specificRelease}.${buildCounter}"
}
else
{
# If the branch starts with "feature-", just use the feature name
$branch = $branch.replace("feature-", "")
$buildNumber = "${majorMinorVersionDevelop}.${buildCounter}-${branch}"
}
Write-Host "##teamcity[buildNumber '$buildNumber']"
Now that %build.number% is based on the branch, your TeamCity build has a consistent build number that can then be used in the rest of your build steps. If you are using OctoPack, for example, the build number can be used as the value of the OctoPackPackageVersion MSBuild parameter so that your NuGet packages match the build number.