In the previous post, you added a custom lifecycle to your project. In this post, you’ll create a mock Kubernetes deployment.
Prerequisites
- An Octopus Cloud account. If you don’t have one, you can sign up for a free trial.
- The Octopus AI Assistant Chrome extension. You can install it from the Chrome Web Store.
The Octopus AI Assistant will work with an on-premises Octopus instance, but it requires more configuration. The cloud-hosted version of Octopus doesn’t need extra configuration. This means the cloud-hosted version is the easiest way to get started.
Creating the project
This example builds on the concepts introduced in previous posts to construct an end-to-end deployment solution to a mock Kubernetes cluster.
Paste the following prompt into the Octopus AI Assistant and run it:
Create a Kubernetes project called "14. Kubernetes with Mock Target", and then:
* Use the container image "octopussolutionsengineering/k8s-mockserver" from the GitHub Docker feed for the "Deploy Kubernetes YAML" step.
* Use client side apply.
* Enable retries on the K8s deployment step.
* Disable verification checks in the Kubernetes steps.
* Retain the "octopussolutionsengineering/octopub-selfcontained" image package reference for the "Deploy Kubernetes YAML" step.
* Use a token account called "Mock Token".
* Use a Kubernetes target with the tag "Kubernetes", the URL http://localhost:48080, using the health check container image "octopussolutionsengineering/k8s-mockserver", using the token account, and the "Hosted Ubuntu" worker pool.The Kubernetes deployment step is configured with an Execution container. Execution containers create the environment where the deployment takes place. Typically, these images contain CLI tools like kubectl to support the deployment.
The octopussolutionsengineering/k8s-mockserver image goes a step further by executing a mock Kubernetes API server on the worker. This server implements just enough of the Kubernetes API to allow testing of deployments without needing access to a real Kubernetes cluster. This is useful for learning and experimentation.
This prompt also creates a Kubernetes target. A deployment process defines how an application is deployed, while targets define where the application is deployed.
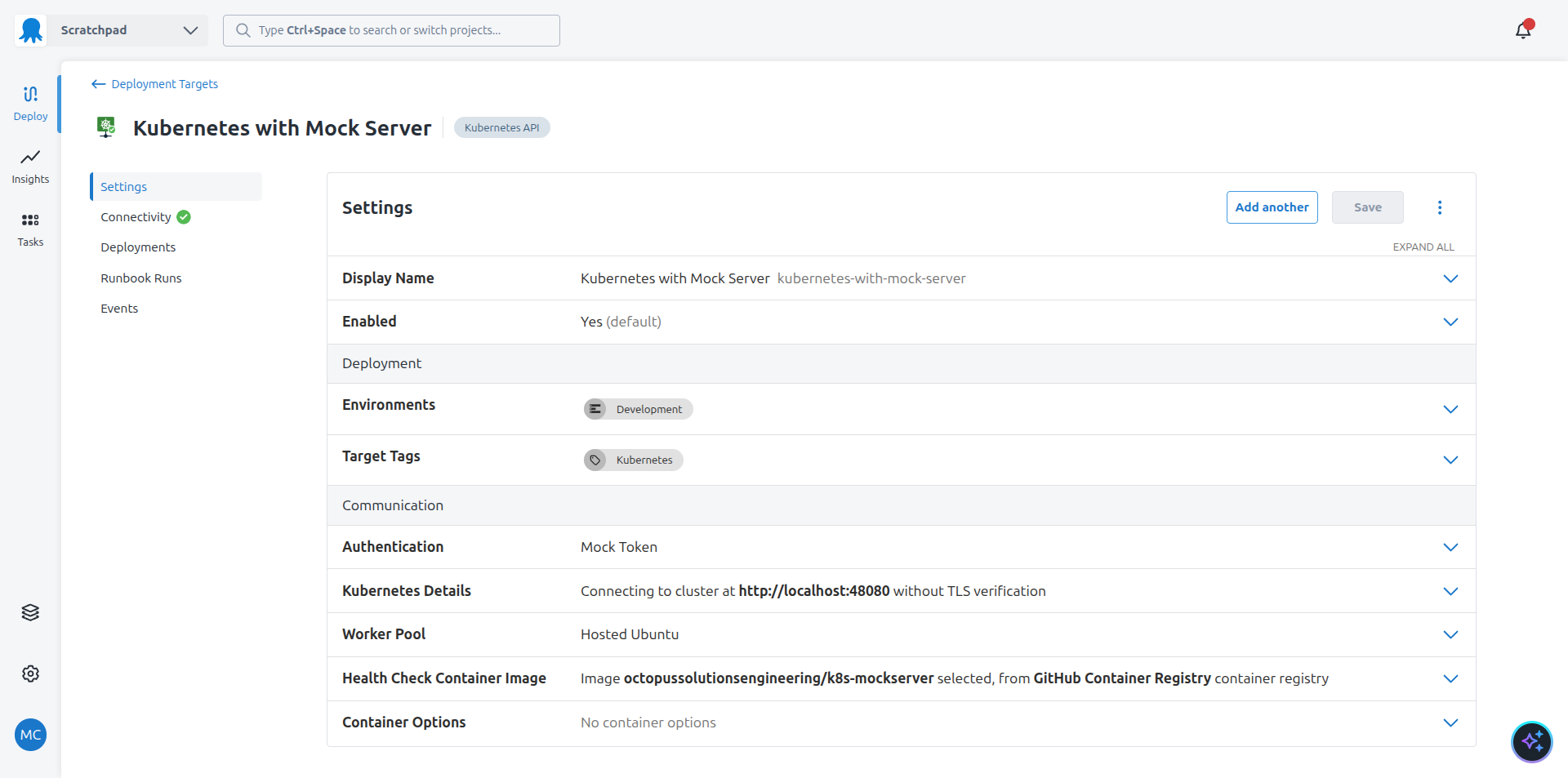
All of these steps run in the Hosted Ubuntu worker pool provided as part of the Octopus cloud platform.
You can interact with the mock Kubernetes server locally by running the following Docker command:
docker run -p 48080:48080 --entrypoint java ghcr.io/octopussolutionsengineering/k8s-mockserver -jar /k8smock/mockk8s.jar
Save the following kubeconfig file to connect to the mock server:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
current-context: local
clusters:
- name: default-cluster
cluster:
server: http://localhost:48080
users:
- name: default-user
user:
token: anything_will_work # the mock server accepts any token
contexts:
- name: local
context:
cluster: default-cluster
user: default-user
namespace: defaultCreate a pod using the mock server:
kubectl run nginx-test --image=nginx --restart=NeverList the pods using the mock server:
kubectl get pods -AYou can now create a release and deploy it to the first environment. The Kubernetes deployment step deploys a Kubernetes deployment resource to the mock Kubernetes server running inside the execution container. Of course, no actual Kubernetes resources are created, but Octopus interacts with the mock server as if it were a real Kubernetes API server.
You will notice that the sample Kubernetes project includes some additional steps. Specifically, it includes a step to scan the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) associated with the sample project. The results of this scan show you if your deployment has any security vulnerabilities.
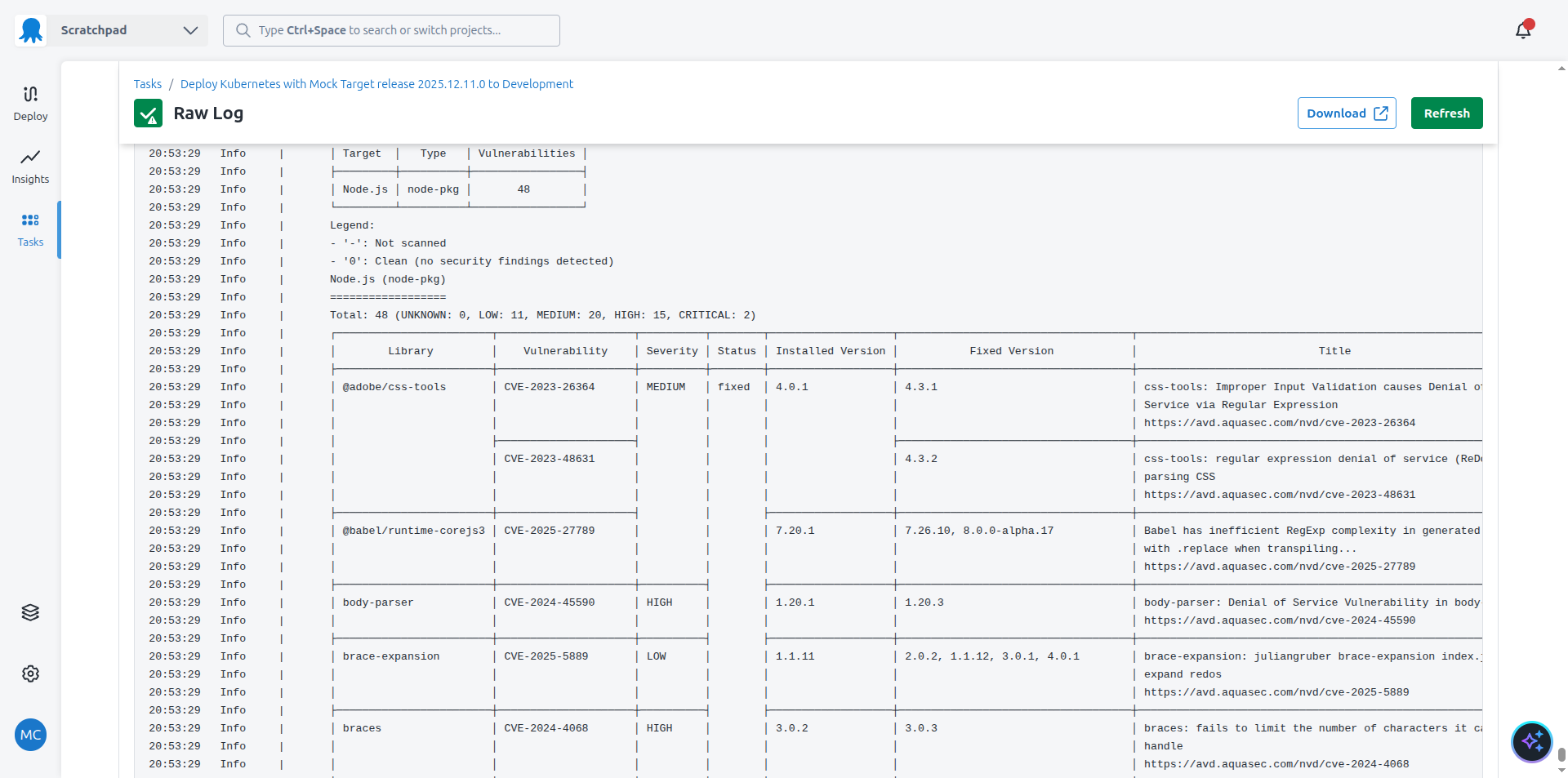
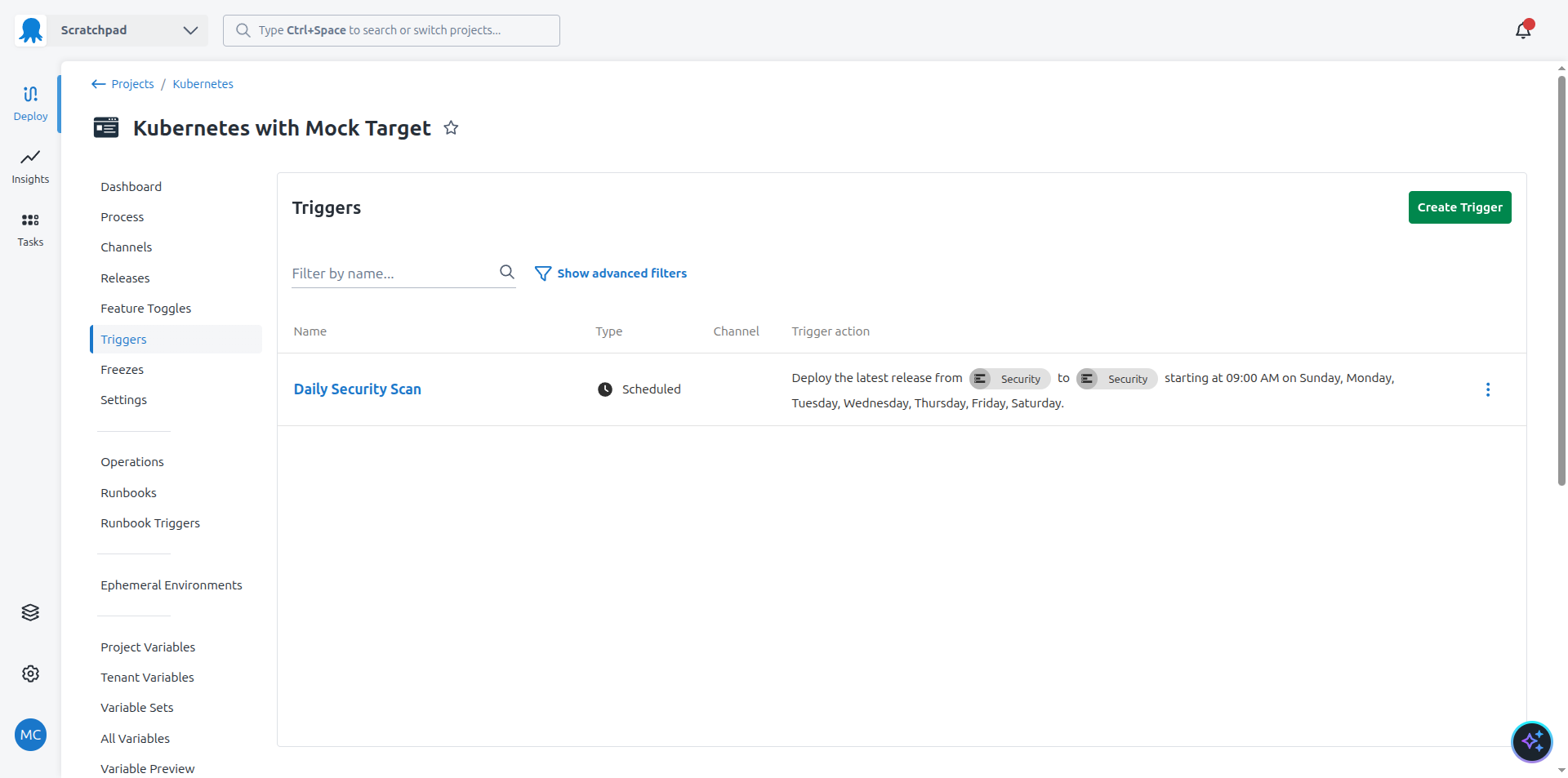
The security scan is executed daily in a dedicated environment called Security using a trigger. This means the SBOM scan result is updated to reflect any new vulnerabilities discovered after a production deployment.
Once the deployment is complete, the execution container is discarded, along with the mock server and any deployed resources.
What just happened?
You created a sample project with:
- A Kubernetes deployment step deploying raw YAML inside an execution container
- A manual intervention with step conditions to only run in the
Productionenvironment - Using step conditions to exclude the deployment step from the
Securityenvironment - A step to scan the SBOM associated with the sample application
- A trigger to rerun the security scan daily
- A Kubernetes target referencing the mock Kubernetes server running inside the execution container




