Octopus supports the deployment of Kubernetes resources through the Deploy Kubernetes YAML step.
This step lets you configure Kubernetes manually, leveraging the full power of Octopus features to support your setup. This approach is more flexible and gives you complete control over the YAML but requires deeper knowledge of Kubernetes configuration.
YAML Sources
You can source your YAML from three different sources:
- Git Repository
- Package
- Inline Script
Git Repository
Sourcing from a Git repository clones the whole repository onto Octopus Server during a deployment. Ensure that you do not have any sensitive data in your git repository.
Sourcing from a Git Repository can streamline your deployment process by reducing the amount of steps required to get your YAML into Octopus. In Octopus, when YAML is sourced from a Git repository, we call it a Git Manifest.
To configure a Git Repository source, select the Git Repository option as your YAML Source.
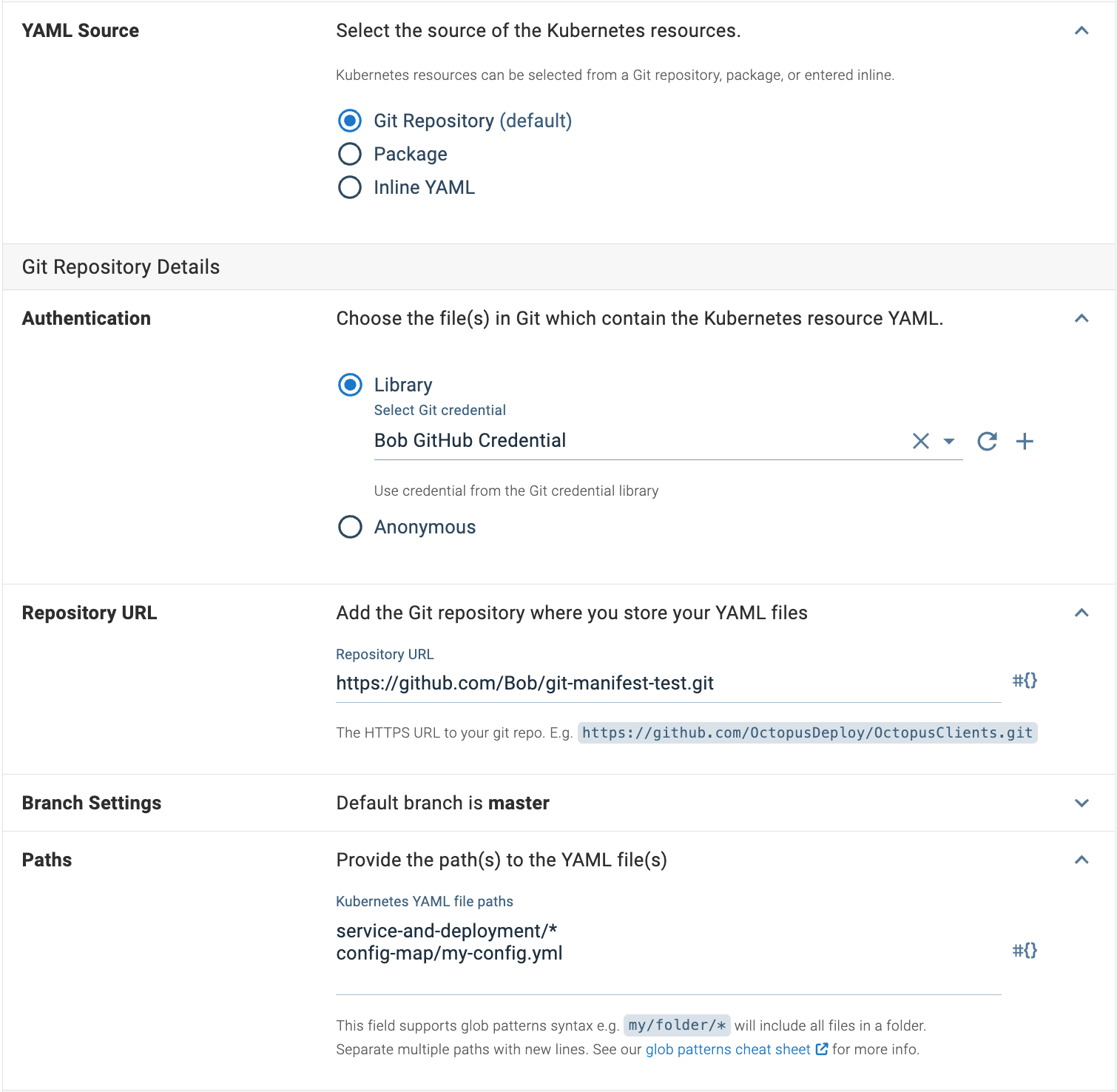
When you choose the tip of a branch for your Git Manifest when creating a Release, the commit hash is saved to the Release. This means redeploying that release will only ever use that specific commit and not the new tip of the branch.
Package
Sourcing from a Package is the traditional way to load data from external sources. You can specify the Package Feed and Package ID as well as a path or paths† to the file(s) in the package that you want to deploy.
To configure a package source, select the Package option as your YAML Source.
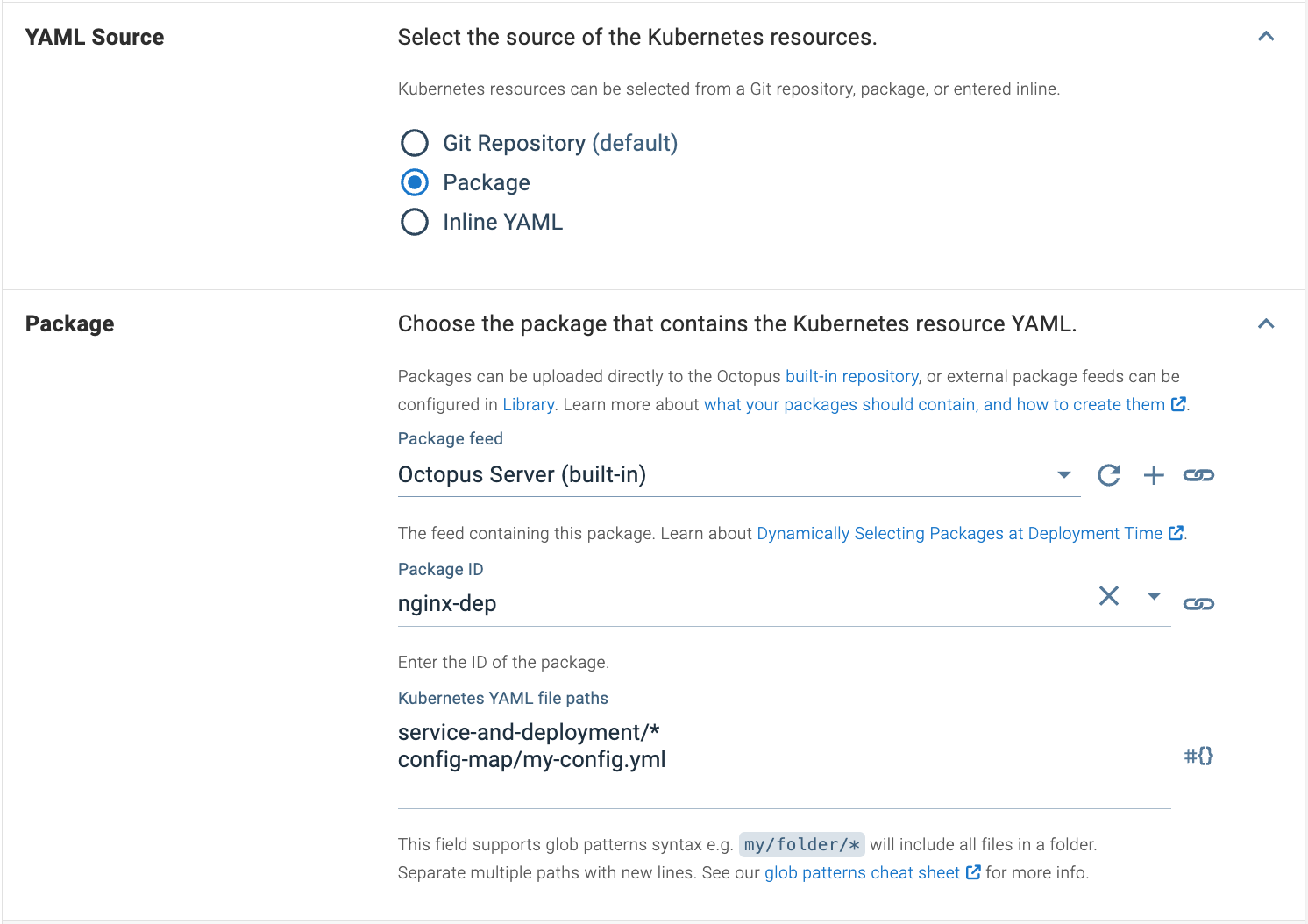
†In 2023.3, sourcing from packages can take advantage of Glob Patterns and Multiple Paths.
Inline YAML
The simplest way to get going with this step is to use Inline YAML. You can create your YAML resources in the inline editor which will be saved in the project in Octopus.
To configure an inline YAML source, select the Inline YAML as your YAML Source.
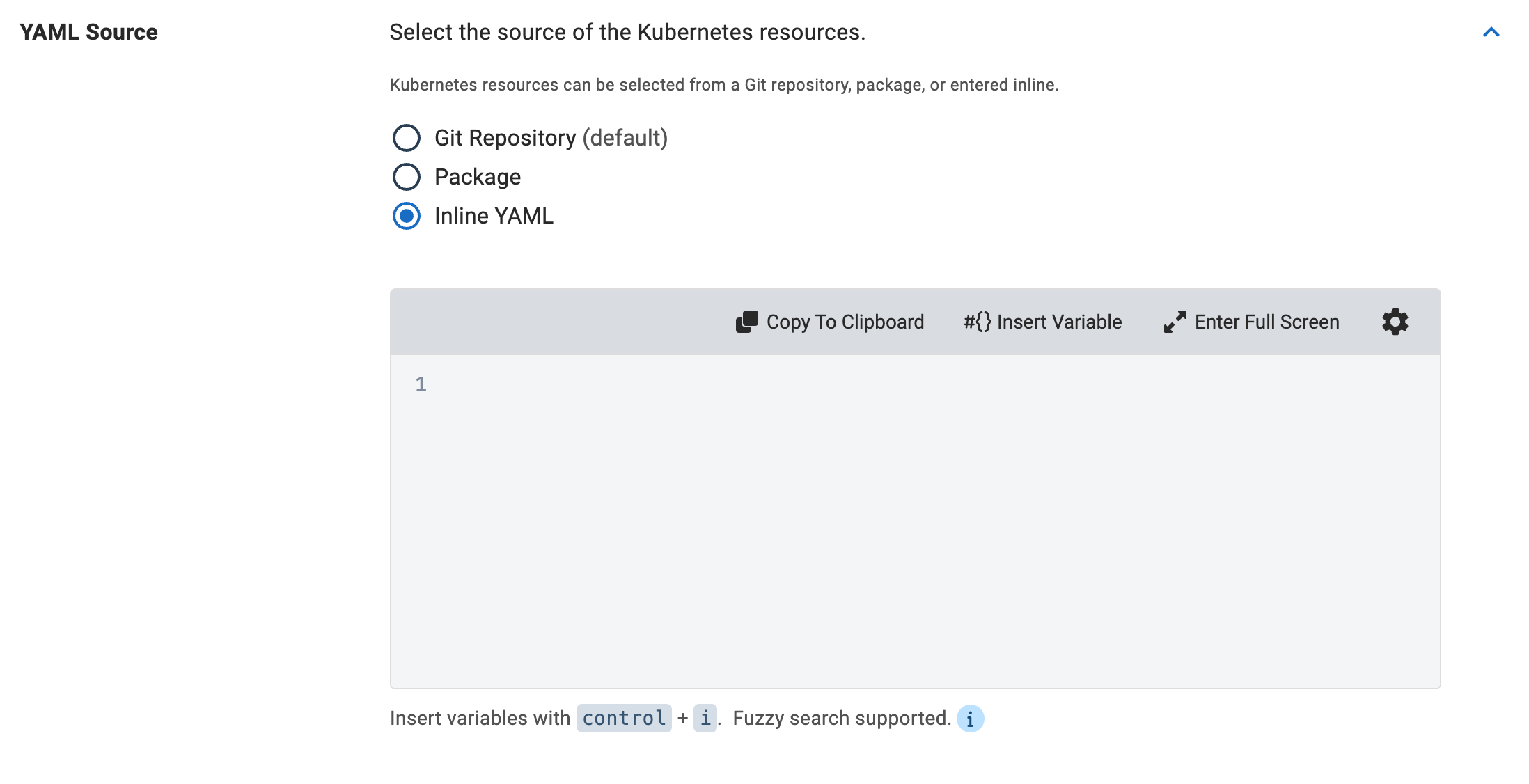
This is not the recommended approach for advanced cases as it does not allow for version management unless you are using it in conjunction with Config As Code.
Referencing packages
Container images can be selected as Referenced Packages to automatically generate variables referring to the image name and tag that can be substituted in your manifests.
For a package with the name nginx, you can substitute the image repository with #{Octopus.Action.Package[nginx].PackageId} and the tag with #{Octopus.Action.Package[nginx].PackageVersion}. The tag is selected when creating the release, allowing you to create new releases without any changes to your YAML manifests.
Automatically creating releases
Using referenced images with your deploy YAML step allow external feed triggers to automatically create releases when one or more new images are pushed to your registries.
Further to this, lifecycles can be used to fully automate deploying your releases to selected environments.
Glob Patterns and Multiple Paths
The Git Repository and Package data sources require you to specify which files you would like to apply from the git repo or package. Previously we only allowed a single file to be applied via an explicit path. In release 2023.3, we have added the ability to source multiple files via multiple paths for both Git Repositories and Packages.
There are a few different ways to take advantage of this feature:
-
You can list several paths by separating them with a new line.
deployments/apply-first.yaml services/apply-second.ymlNote: Each path will be applied in order from top to bottom.
-
You can use a glob pattern to select multiple files in a single path.
**/*.{yaml,yml}Note: All files matching a glob pattern will be applied at the same time.
-
Both options at the same time. This gives you the best of both worlds!
Note: If multiple glob patterns find the same file, the file will be applied twice.
Learn more about glob patterns.
Step updates
2024.1:
Deploy Raw Kubernetes YAMLwas renamed toDeploy Kubernetes YAML.- If you store your project configuration in a Git repository using the Configuration as code feature, you can source your YAML from the same Git repository as your deployment process by selecting Project as the Git repository source. When creating a Release, the commit hash used for your deployment process will also be used to source the YAML files. You can learn more in this blog post.
2023.3:
- Sourcing from Git Repositories was added. You can learn more in this blog post.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Thursday, November 7, 2024