Octopus lets you map and organize your infrastructure, keeping it separate from your deployment process. Instead of hard-coding machines or resource names in your process, you can configure steps to run on targets based on tags called target tags. This means you don’t have to change your deployment process when you add or remove hosting resources.
You assign deployment targets to an environment and you can set up a lifecycle that represents the sequence of environments.
Target tags also make applying the same process to all environments easier. The table below shows a matrix of target tags and environments, with environments having different resource sets. Deployments proceed in an orderly fashion across the matrix.
Development | Staging | Production | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web tag | Dev-Target-1 | Staging-Target-1 Staging-Target-2 | Production-Target-1 Production-Target-2 Production-Target-3 |
| API tag | Dev-Target-2 | Staging-Target-3 Staging-Target-4 | Production-Target-4 Production-Target-5 |
| Database tag | Dev-Target-3 | Staging-Target-5 | Production-Target-6 Production-Target-7 |
You can manage the machines and services you deploy your software to on the Infrastructure tab of the Octopus Web Portal:
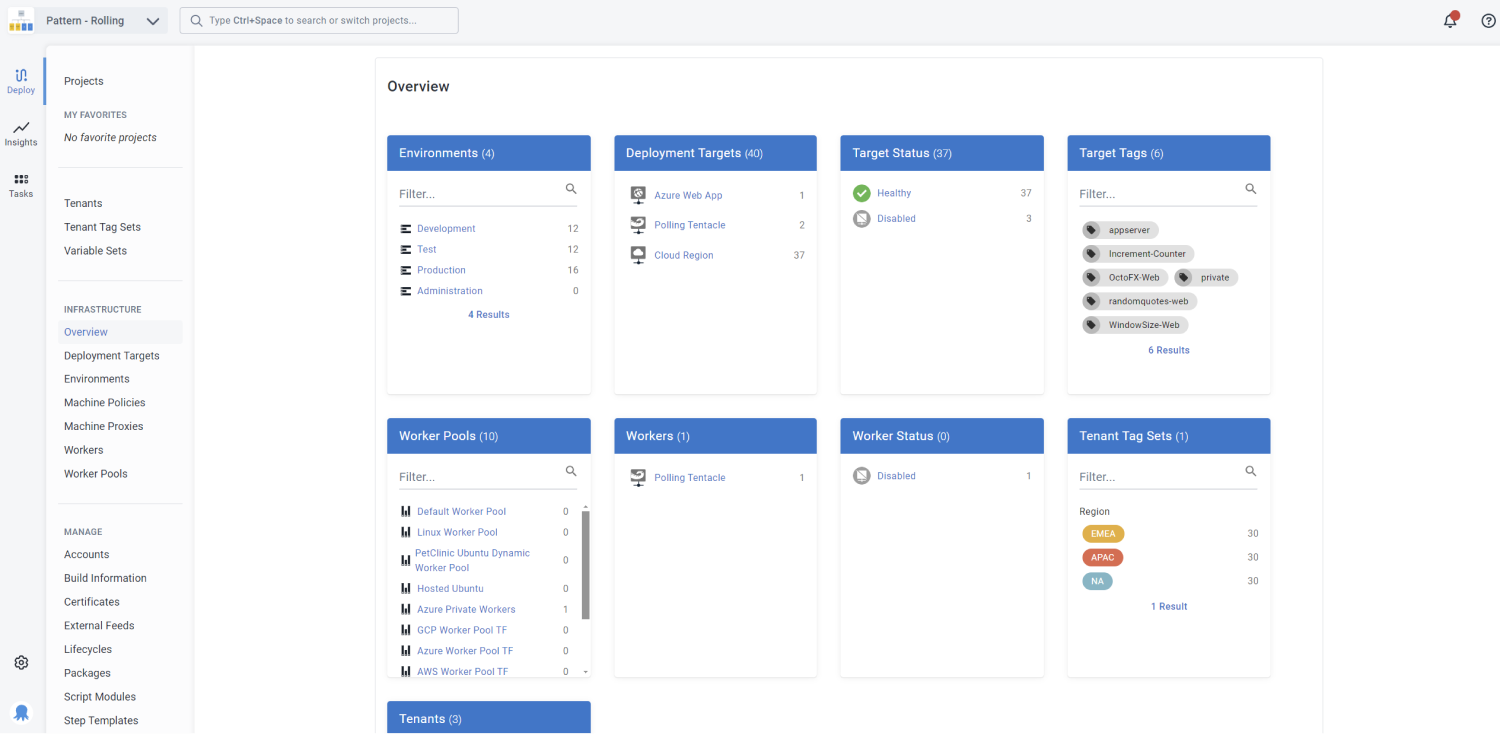
There are a few key infrastructure concepts in Octopus Deploy:
- Environment: The infrastructure used to run software for a specific purpose, like testing, staging, or production.
- Lifecycle: A sequence of environments through which software progresses to production.
- Phase: An ordered step in a lifecycle, with environments and progression rules.
- Deployment target: A server, platform, or serverless function that runs your software.
- Tentacle: A lightweight deployment agent that runs on Windows or Linux servers.
- Target tag: A tag that defines a purpose for the deployment target, which can be used to deploy particular components to a set of targets.
Learn more
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Thursday, June 27, 2024