By configuring your Octopus project with container dependencies, you can now create triggers that watch those repositories for new packages, container images and Helm charts pushed by your build tool. This feature enables pull-driven deployments for Kubernetes steps. Based on tags and version rules, triggers detect if an image appears that is later than the image used in your previous release. Octopus then automatically creates a new release with all the latest container images or Helm Chart dependencies.
Your existing lifecycles will then promote that release through your environments or tenants, just like it does currently. If your lifecycle uses automatic release progression, then you’ve just set up a Continuous Delivery pipeline without explicitly letting Octopus know about your application changes!
The details of these container images and Helm Charts are already known in Octopus. This means we can use the registry locations, image names, chart names, and credentials to do this monitoring, without adding or maintaining this information anywhere else.
Common use cases
-
Automated deployments with Helm charts
Create releases when any referenced images used in your Helm charts are updated.
-
Tracking third party Helm charts
Create releases whenever a third party releases a new Helm chart.
-
Deployments with YAML manifests
Create releases for a deployment referencing any number of images.
Getting started
Navigate to your project and click Triggers. Click Add Trigger on the right-hand side of the page, and select External feed.
Enter a name and description for your trigger. The name should be short, memorable, and unique. Example: Nginx Docker Update.
Channels and lifecycles
If your project contains multiple channels, you have the option of selecting which channel this trigger will apply to. Any pushed packages must satisfy the selected channel’s versioning rules to trigger release creation. The releases created by the trigger will use this channel.
The versions used for those releases is guided by release versioning under Settings. They will use the rules defined there.
Unlike the existing built-in package repository triggers (formerly Automatic Release Creation), you can create multiple external feed triggers per project. This can enable you to automatically create releases for multiple channels.
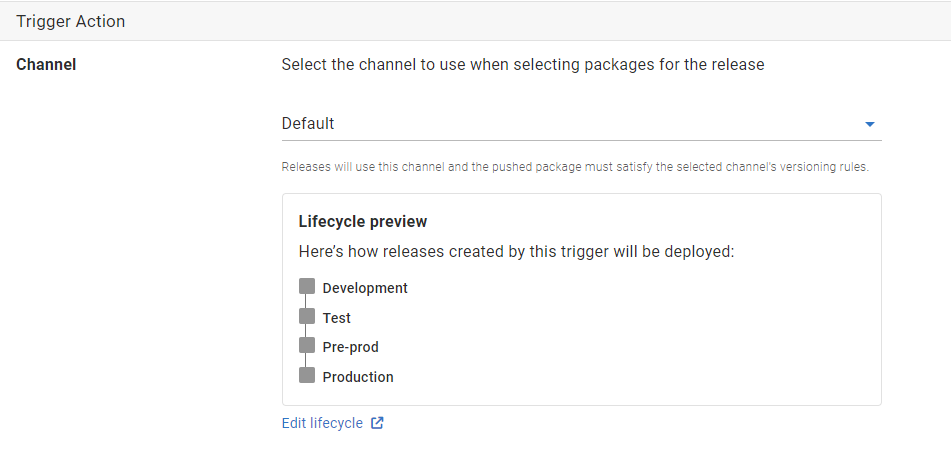
A preview of the lifecycle used by the selected channel is displayed. You can modify the lifecycle’s phases to have a release created and deployed to selected environments whenever a new package is pushed.
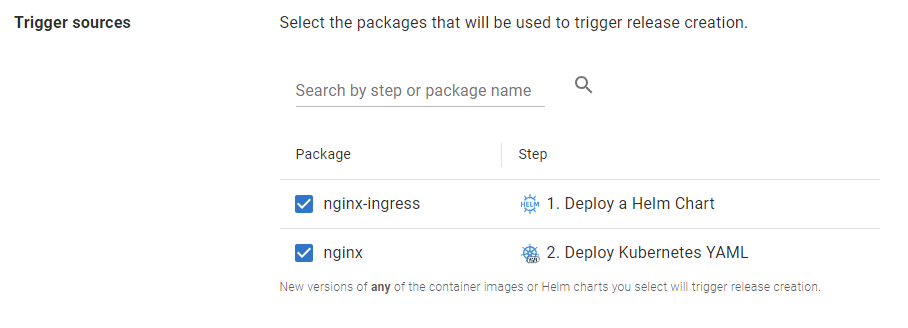
Trigger sources
Any container images or Helm Charts referenced in your project’s deployment process can be selected to trigger release creation.
Please note that for configuration as code projects, only container images and Helm Charts in the deployment process from the default branch are able to be referenced. Any changes to the deployment process in other branches will not be available for use in external feed triggers.
History
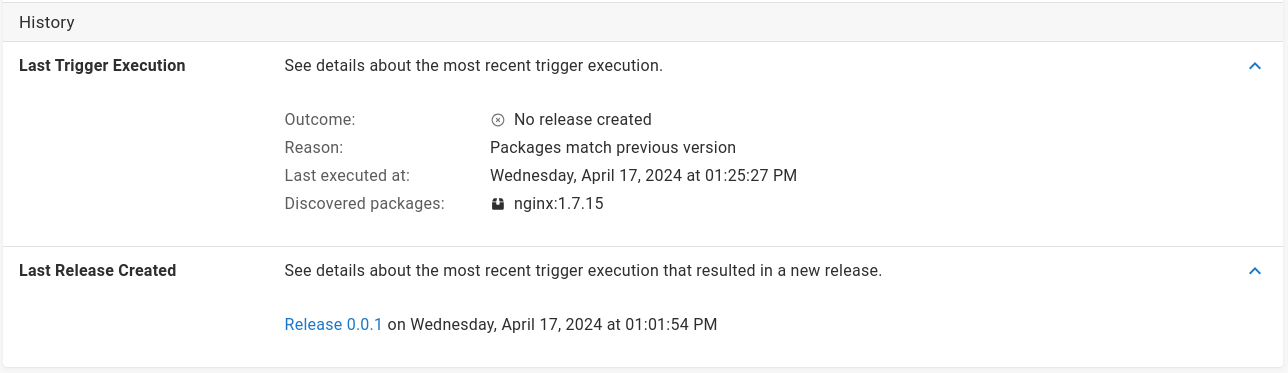
The history section contains information about the last time the trigger was evaluated and the last release that was created by the trigger. By default, triggers are evaluated every three minutes and results will be reported here.
- Outcome: Tells you if there was any action taken, or if there was an error during processing.
- Reason: Additional information about the outcome.
- Last executed at: The time the task was run.
- Discovered packages: A full list of watched packages, container images or Helm charts and the versions that were found in this execution.
If the trigger has created a release, a link to the created release will be shown alongside the date it was created.
If required, more detailed information can be found in the system task logs.
Advanced use cases
Feeds or packages referenced using variable substitution are able to be leveraged with external feed triggers. They will only be used by the trigger, however, if they are evaluated as either container or Helm Chart repositories, and also do not use variable unavailable at release creation time. For example, using an environment name variable will not work, because that value is only available at the time of deployment.
If you have a chain of dependencies with your external feed packages, make sure your trigger uses the package which will be pushed to its repository last.
Troubleshooting
When you are using external feed triggers there are a few reasons why a release may not be created successfully. Take some time to consider the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Inspect the task list for errors in the Task menu - Octopus will log the reason why external feed triggers failed as errors or warnings. Note that external feed triggers are system tasks, and do not display in the list by default. Use the Show advanced filters option and select Include system tasks to show them.
-
Ensure you are pushing the package to a supported external feed type. While capability has been verified against most major Docker providers, compatibility is not guaranteed - please contact Octopus Deploy support if you encounter any problems.
-
Ensure that packages in the external feed match the channel rules if defined for the trigger’s channel (or the default channel if your project doesn’t have multiple channels). Triggers will only create a new release if the packages match channel rules.
-
Ensure you are pushing a new version of the package - Octopus will not create a release where the package has already been used for creating a release.
-
Ensure you are pushing a package that Octopus will consider as the latest available package. The trigger’s version evaluator uses SemVer, and will not trigger off image tags such as ‘latest’.
-
Make sure that the feed and package references only use variables which are able to be evaluated at release creation time. For example, the environment name variable is not available, because it is only known at the time of deployment.
-
If you have a chain of package dependencies with your external feed packages, make sure your trigger uses the package which will be pushed to its repository last. Otherwise, some of the packages required for the release may be missing.
-
As mentioned above, for configuration as code projects, only container images and Helm Charts in the deployment process from the default branch are able to be referenced. Any changes to the deployment process in other branches will not be available for use in external feed triggers.
Learn more
Take a look at the Octopus Guides which covers building and packaging your application, creating releases and deploying to your environments for your CI/CD pipeline.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Wednesday, August 28, 2024