What is Octopus Deploy?
Octopus Deploy is an automated deployment and release management platform that helps teams deliver software consistently and repeatedly. It bridges the gap between Continuous Integration (CI) and production environments by orchestrating deployments, handling configuration variables, and managing release lifecycles. Octopus Deploy integrates with CI servers like Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and TeamCity, automating the final steps of application delivery.
Octopus Deploy promotes best practices like environment separation, variable scoping, and deployment auditing. It supports deployment patterns for microservices, monoliths, and hybrid architectures across on-premises or cloud targets. With automation of approvals, scheduling, and multi-phase rollouts, Octopus Deploy reduces manual interventions and minimizes release risks for DevOps teams aiming for reliable, consistent delivery cycles.
Several popular alternatives exist for Octopus Deploy, offering similar CI/CD and deployment automation capabilities. Some of the top contenders include CloudBees CD/RO, Harness, and GitLab. We’ll review 7 of these options and explain how they are different from Octopus. We’ll also review another common alternative, taking a DYI approach and building deployment automation in-house.
This is part of a series of articles about Continuous Deployment
Key features of Octopus Deploy
Octopus Deploy automates, controls, and manages deployments across diverse environments. It combines deployment orchestration with operational automation, enabling teams to ship faster while reducing risk and ensuring consistency.
Key features
- Centralized DevOps automation: Automates both deployments and operations runbooks from one platform, reducing manual effort and eliminating handoffs between development and operations.
- Broad platform and integration support: Works with popular CI tools such as Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and TeamCity, adding deployment and operational automation to complete the CI/CD pipeline.
- Configurable deployment processes: Allows teams to define deployment steps once and reuse them across environments such as virtual machines, Kubernetes namespaces, and cloud services.
- Environment and variable management: Supports scoped variables so that one deployment process can adapt to multiple environments without hardcoding configuration. Sensitive data such as passwords are stored securely.
- Promotion across environments: Enables controlled promotion of releases from development through testing and into production, aligning with real-world release practices.
- Real-time deployment visibility: A dashboard shows which application versions are deployed to each environment, removing uncertainty about release states.
- Extensive step library: Offers over 550 built-in deployment steps, covering tasks like sending notifications, running scripts, updating CDNs, and executing database changes.
- Multi-platform deployment targets: Supports deployments to physical servers, VMs (via Tentacle agent), containers, and serverless platforms across on-premises, hybrid, and cloud infrastructures.
- Runbook automation: Provides a runbook engine to automate both routine and emergency operational tasks, with scheduling, auditing, and environment targeting.
- Configuration as code: Integrates with Git for version control of deployment processes, allowing changes in either Octopus UI or text editors, with branching, reviewing, and merging supported.
- Deployment practices: Encourages build-once, process consistency, minimal downtime (via blue-green, canary, or rolling deployments), and low-code/no-YAML configuration.
- Flexible networking and security: Tentacle agent supports TLS encryption, certificate authentication, SSH, proxies, and advanced network topologies for secure and adaptable connectivity.
- Optimized VM deployment: Includes features like remote delta compression to reduce deployment bandwidth and speed up delivery to VMs.
- Multi-tenancy support: Manages deployments for multiple customers or groups without duplicating processes, ensuring scalability for service providers.
Notable Octopus Deploy alternatives
1. DIY, 100% homegrown solution
A homegrown deployment solution is built and maintained entirely in-house, often starting from scripts and internal tools. The main draw is that it’s free from a licensing perspective; there is no procurement process and full control over customization to match exact internal needs. If requirements stay static and the team has strong in-house expertise, a DIY tool can appear cost-effective and aligned to current workflows.
Key capabilities
- Full customization: Tailored to the environment and needs.
- Zero licensing cost: No fees for purchasing or renewing software.
- Tight integration: Direct alignment with existing internal tools and workflows
How Octopus Deploy compares
While DIY tooling can work in limited, stable scenarios, Octopus addresses its biggest long-term weaknesses:
- Hidden costs: Although free to license, DIY tools incur significant people-hours for updates, bug fixes, audits, and adapting to new technologies or compliance requirements.
- Knowledge risk: Often, only a handful of maintainers understand how the tool is “strung together.” If they leave, continuity suffers.
- Feature completeness: DIY solutions typically lack native support for environment modeling, immutable releases, multi-tenancy, Day 2 runbooks, and pipelines-at-scale, all of which Octopus provides out of the box.
- Breadth of target support: Octopus deploys to Kubernetes, PaaS, VMs, heritage apps, and edge environments securely. DIY tools are usually built for a narrower set of targets and require heavy rework to expand.
- Scalability & governance: Updating hundreds or thousands of pipelines when tooling or policies change is nearly impossible without Octopus’ blueprints and guardrails.
- Operational reliability: Octopus includes enterprise-grade RBAC, SSO, ITSM integration, and auditable approvals, reducing the risk of compliance failures and downtime.
2. ArgoCD (Vanilla)
ArgoCD is an open-source GitOps tool for deploying applications to Kubernetes. In its vanilla form, it synchronizes manifests from Git repositories into Kubernetes clusters, making it a popular option for teams running cloud-native workloads. It’s free from a licensing standpoint and considered a standard for Kubernetes GitOps, offering customization options for cluster-focused delivery pipelines.
Key features:
- Kubernetes GitOps delivery: Uses Git as the single source of truth and automatically synchronizes state to clusters.
- Pull‑based reconciliation: Continuously monitors and enforces desired state, reverting unauthorized changes.
- Declarative manifests support: Works with Helm, Kustomize, Jsonnet, and plain YAML.
- Monitoring and rollback: Detects drift and allows rollback to prior states.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
While ArgoCD is useful for Kubernetes-specific delivery, it lacks the breadth and enterprise features Octopus provides:
- Application type coverage: ArgoCD supports only Kubernetes. Octopus handles Kubernetes, PaaS, VMs, heritage applications, and edge deployments with secure multi-tenancy.
- End-to-end release management: Vanilla ArgoCD doesn’t natively provide immutable releases, environmental promotion, or DRY deployment processes across environments, all of which Octopus includes out of the box.
- Day 2 operations: Routine production tasks like restarting services, provisioning/de-provisioning, or gathering logs require separate tooling in ArgoCD. Octopus delivers this via runbooks.
- Enterprise compliance & governance: Octopus integrates with ITSM and SIEM systems, supports fine-grained RBAC and SSO, and offers blueprints and guardrails to update pipelines at scale. Vanilla ArgoCD requires manual assembly of these capabilities.
- Visibility and scalability: Octopus gives a single pane of glass for all deployments across all environments and app types. ArgoCD is limited to Kubernetes clusters and lacks unified cross-platform release views.
- Support model: Octopus offers 24/7 enterprise-grade support and a 99.99% uptime SLA. ArgoCD users assume all operational responsibility for running and troubleshooting the platform.
![]()
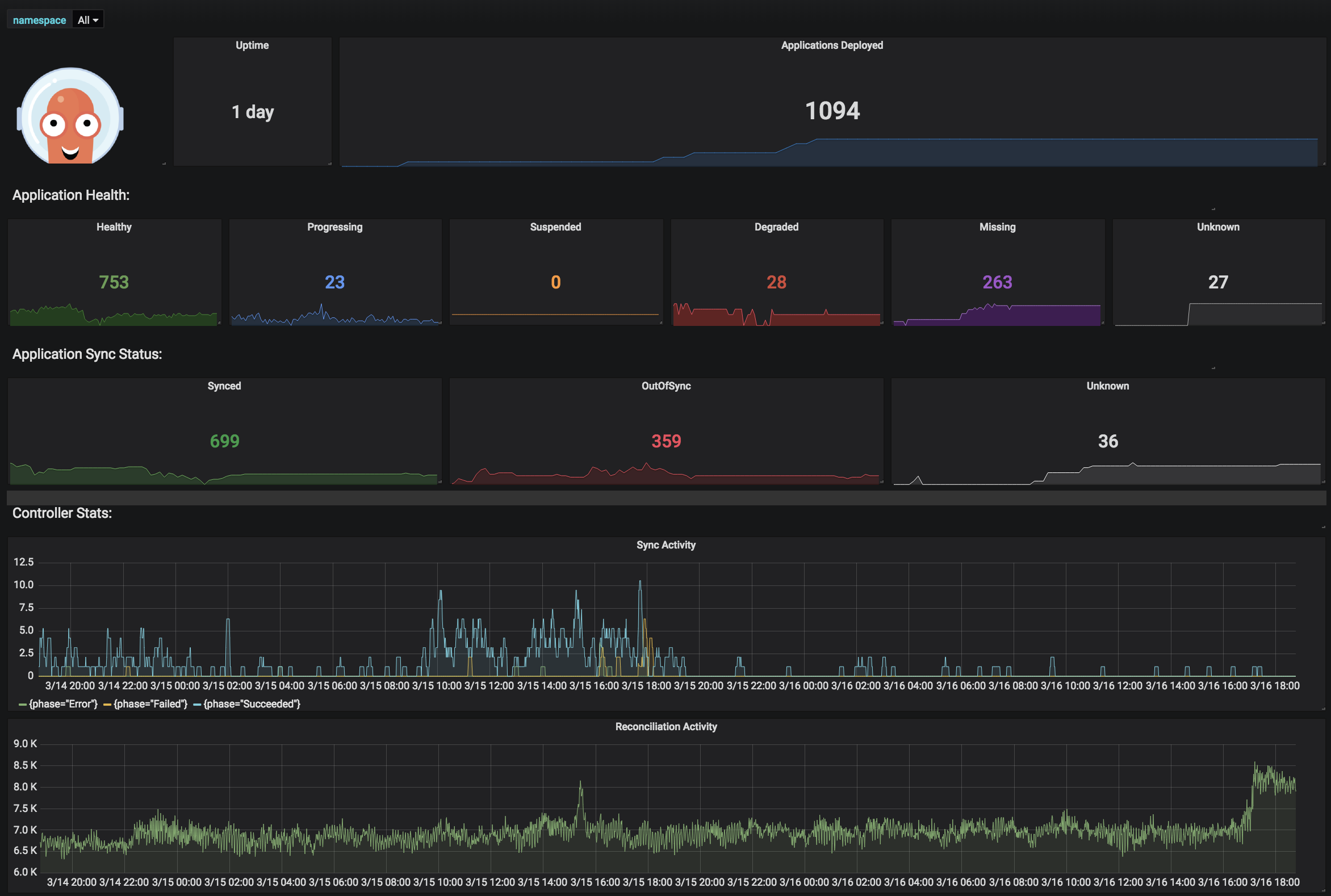
Source: Argo CD
3. CloudBees CD/RO
CloudBees CD/RO is an enterprise release orchestration and Continuous Delivery platform aimed at managing complex deployments across modern and heritage applications. It can handle Kubernetes, PaaS, and VM-based workloads, and is often positioned for large organizations needing pipeline modeling, release governance, and CI/CD process integration.
Key features:
- Release orchestration at scale: Automates complex deployments across teams, tools, and environments.
- Dashboard visibility & metrics: Includes release calendars, dashboards, DORA metrics, and CI/CD insights.
- Process‑as‑code: Supports modeling with Groovy or YAML DSLs, APIs, and integrations.
- High availability & clustering: Designed for enterprise scalability and resilience.
- Model-driven environment targeting: Decouples “what, where, and how” to allow targeting across endpoints like AWS or GCP.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
While CloudBees CD/RO can manage sophisticated pipelines, Octopus provides stronger out-of-the-box coverage for diverse enterprise deployment needs:
- Multi-tenancy and edge support: Octopus includes built-in multi-tenancy for SaaS and edge deployments, while CloudBees lacks native support in these areas.
- Immutable releases and environmental progression: Octopus natively supports immutable release snapshots and structured promotion across environments; CloudBees requires more manual configuration to achieve the same.
- Day 2 operations: Octopus offers runbooks for operational tasks like service restarts, log retrieval, and provisioning; CloudBees does not provide equivalent built-in capabilities.
- Pipelines at scale: Octopus’ blueprints and guardrails enable centralized updates across hundreds or thousands of pipelines when compliance or tooling changes, whereas CloudBees lacks an equivalent large-scale update mechanism.
- Breadth of application target support: Octopus supports Kubernetes, PaaS, heritage apps, and edge locations equally, while CloudBees’ capabilities depend on tooling integration and may require additional setup for non-modern workloads.
- Operational model: Octopus provides a 99.99% uptime SLA and 24/7 enterprise support. CloudBees’ support hours and responsiveness vary by severity level and plan.
![]()
Source: CloudBees
4. Harness
Harness is a software delivery platform that covers the SDLC from CI/CD to cloud cost management, and feature flags. It appeals to executives by promising a single tool that reduces context switching and consolidates responsibilities under one vendor. The onboarding is highly polished, offering templates to quickly set up pipelines across teams, and it carries enterprise compliance certifications like FedRAMP, CCPA, and CSA Star. Its Kubernetes deployment capabilities are built on top of Argo, but it wraps additional tooling and integrations around it.
Key features:
- Reusable templates: Define and enforce deployment patterns across teams.
- Built-in deployment strategies: Canary, blue‑green, rolling, available across Kubernetes, VMs, and serverless.
- Full platform scope: Includes CI/CD, feature flags, cloud cost management, infrastructure provisioning, and security orchestration.
- Modular platform: Teams can adopt specific modules as needed.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
While Harness spreads its focus across many modules, Octopus Deploy is purpose-built for Continuous Delivery at scale. This focus gives Octopus several advantages:
- Depth over breadth: Octopus concentrates on deployment automation and complex release management rather than trying to cover every stage of the SDLC. This avoids the “MVP” or “good enough” quality seen in all-in-one modules.
- Complex deployment support: Octopus handles multi-environment progression, immutable release snapshots, runbooks for Day 2 operations, and multi-tenancy out of the box. These are areas where Harness has limited or no native support.
- Broader deployment targets: Octopus supports modern (Kubernetes, PaaS) and heritage (Windows/Linux VMs, edge) environments equally well, whereas Harness requires more workarounds for non-Kubernetes targets.
- Scalability & maintainability: Octopus allows defining a deployment process once and reusing it everywhere. Its blueprints and guardrails enable pipelines at scale and easy updates when tooling or compliance changes, something Harness lacks for long-term pipeline evolution.
- Integration-first approach: Instead of competing with other best-in-breed tools, Octopus integrates deeply with CI servers, ITSM, SIEM, and IaC solutions, giving teams flexibility to choose the best components for their stack.
- Operational reliability: Octopus offers a 99.99% uptime SLA and 24/7 enterprise support, surpassing Harness’s 99.8% uptime and limited 9–5 PST support for many cases.
![]()
Source: Harness
5. GitLab
GitLab is a DevOps platform combining source code management, CI/CD, issue tracking, and security scanning in a single application. Its open-core model allows teams to start with a free version and upgrade to paid tiers for enterprise capabilities. GitLab appeals to organizations that want their source control, pipelines, and collaboration tools in the same place, with a unified UI and tight Git integration.
Key features:
- End‑to‑end DevOps platform: Combines SCM, CI/CD, issue tracking, and security scanning.
- Repo-centric pipelines: YAML-based pipeline configuration directly in repos.
- Flexible hosting: Offered in both self-hosted and SaaS forms.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
While GitLab’s CI/CD features work well for straightforward delivery pipelines, its deployment capabilities are limited compared to Octopus:
- Depth of deployment automation: GitLab’s pipelines are repository-focused and lack native features like multi-tenancy, immutable release snapshots, or reusable deployment processes across all environments.
- Complex delivery support: Advanced scenarios such as edge deployments, hybrid cloud rollouts, and heritage application releases require more manual scripting and workarounds.
- Scalability & governance: GitLab does not offer a single pane of glass to monitor deployments across all projects, making enterprise-wide visibility and compliance harder to achieve.
- Best-of-breed integrations: Octopus integrates deeply with GitLab CI for builds while providing richer release management, environmental progression, and Day 2 operational automation.
- Enterprise operational readiness: Octopus offers stronger support for pipelines at scale, with blueprints and guardrails to quickly update processes when regulations, tools, or best practices change.
![]()
Source: GitLab
6. Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps is Microsoft’s integrated suite of development tools, offering version control, CI/CD pipelines, work item tracking, and artifact management. It is often included at no additional cost in enterprise Microsoft agreements, making it an attractive option for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Key features:
- Integrated toolchain: Combines source control, CI/CD, work tracking, and package management in one suite.
- Pipeline automation: YAML or GUI-based pipeline definitions for build and release workflows.
- Artifact storage: Built-in support for NuGet, npm, Maven, and universal packages.
- Permissions and approvals: Supports RBAC and manual approvals within project pipelines.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
While Azure DevOps covers a broad set of development lifecycle features, its deployment automation is less capable for complex or large-scale delivery:
- Focus and depth: Azure DevOps’ pipelines are project- and repo-centric, lacking a single pane of glass for managing deployments across multiple applications and environments.
- Advanced deployment capabilities: Native support for multi-tenancy, immutable releases, and Day 2 operational runbooks is missing, requiring manual workarounds or external tools.
- Hybrid and edge readiness: Although it can deploy to on-premises targets, these scenarios are less streamlined compared to Octopus’ secure agent model and built-in multi-tenancy.
- Scalability for change: Azure DevOps does not provide a robust pipelines-at-scale solution. Updating 100s or 1000s of pipelines when compliance rules or tooling changes can be labor-intensive without Octopus’ blueprints and guardrails.
- Specialization vs. generalization: Octopus is dedicated to Continuous Delivery, enabling complex deployments, environmental progression, and risk reduction as core capabilities, while Azure DevOps spreads focus across many unrelated modules.
![]()
Source: Azure DevOps
7. GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD automation service built into GitHub, allowing developers to run workflows triggered by repository events. It’s widely adopted because of GitHub’s dominance in source control, and it offers a low barrier to entry for teams already hosting their code on the platform. Adding deployment steps is “free” from a licensing perspective, aside from usage-based runner and storage costs, and it works well for simple pipelines, especially in dev and test environments.
Key features:
- Event-driven workflows: Trigger actions on pushes, pull requests, and scheduled events.
- YAML-based configuration: Define CI/CD workflows in code alongside source repositories.
- Built-in runner support: Supports Linux, Windows, and macOS runners, with options for self-hosted agents.
- Extensible actions library: Thousands of community-contributed steps available via GitHub Marketplace.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
While GitHub Actions is convenient for lightweight deployment tasks, it lacks the depth and enterprise-scale capabilities Octopus provides:
- Deployment specialization: GitHub Actions is primarily a CI and automation tool. Complex CD concepts like multi-tenancy, immutable releases, and reusable deployment processes across all environments are not native.
- Scalability & governance: Pipelines are repository-focused, with no single pane of glass for monitoring releases across applications and environments, making compliance and change management more difficult at scale.
- Operational readiness: Day 2 operations, environment progression, and advanced release strategies require heavy custom scripting, increasing maintenance overhead.
- Broad target support: Octopus natively handles Kubernetes, PaaS, VMs, heritage apps, and edge deployments with secure agents, while GitHub Actions often needs separate runners or external integrations for non-cloud-native targets.
- Reduced maintenance risk: Octopus’ blueprints and guardrails make it possible to update hundreds or thousands of pipelines when tooling or compliance requirements change, avoiding the script sprawl common in GitHub Actions setups.
![]()
Source: GitHub Actions
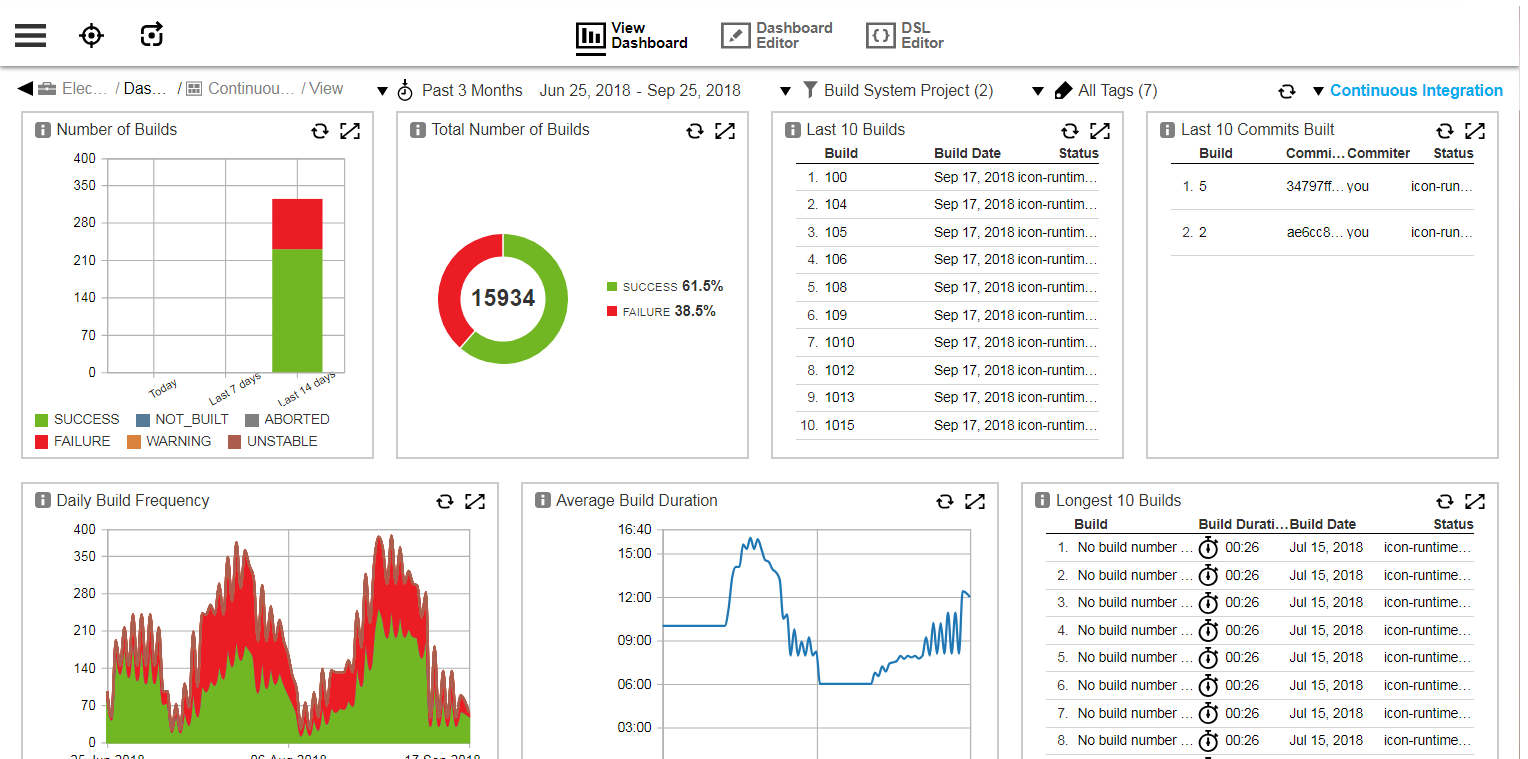
8. Jenkins
Jenkins is a long-standing, open-source automation server used for Continuous Integration. It is extensible through plugins and has become the de facto CI server for many organizations, especially those with deep in-house expertise. Since it’s free from a licensing standpoint, teams often extend Jenkins to run deployments, adding scripts and jobs to push code to environments. For simple scenarios, especially in dev and test, this can be a cost-effective approach.
Key features:
- Scripted or declarative pipelines: Define automation using Groovy-based DSL.
- Self-hosted flexibility: Can run on any infrastructure with customizable resource usage.
- Community-driven: Open-source with broad documentation and community support.
- Build-centric model: Primarily focused on CI tasks, with add-on capabilities for CD via plugins and scripting.
How Octopus Deploy compares:
Using Jenkins as a deployment platform introduces challenges that Octopus is purpose-built to solve:
- Deployment specialization: Jenkins lacks native concepts like environment promotion, immutable releases, and reusable deployment processes across all environments, forcing teams to script these features manually.
- Maintenance overhead: Homegrown deployment logic in Jenkins demands ongoing upkeep, with significant risk if key maintainers leave.
- Complex delivery scenarios: Edge deployments, hybrid-cloud rollouts, and heritage application releases are not first-class citizens in Jenkins, often requiring fragile workarounds.
- Security and compliance: Octopus includes fine-grained RBAC, SSO, ITSM integration, and auditable approvals out of the box. Replicating this in Jenkins requires extensive custom development.
- Pipelines at scale: Octopus’ blueprints and guardrails enable updating hundreds or thousands of deployment processes in line with changing compliance, tooling, or best practices; something Jenkins cannot do natively.
- Operational readiness: Octopus provides Day 2 runbooks, multi-tenancy, and multiple Kubernetes deployment options, while Jenkins focuses primarily on build orchestration.
![]()
Source: Jenkins
Summary: Octopus Deploy alternatives and how they compare
| Solution | Key Features | How It Compares to Octopus Deploy |
|---|---|---|
| DIY Homegrown | Custom tooling, no license fees, internal integration | High maintenance, lacks built-in CD features, not scalable or auditable |
| ArgoCD (Vanilla) | Kubernetes GitOps, declarative manifests, drift detection | Kubernetes-only, no release promotion, Day 2 automation, or enterprise governance |
| CloudBees CD/RO | Enterprise orchestration, dashboards, DSL modeling | Limited support for edge/multi-tenant delivery, lacks native runbooks or blueprints |
| Harness | Modular SDLC platform, prebuilt strategies, feature flags | Broad but shallow, less support for heritage/edge, lacks CD depth and pipeline maintainability |
| GitLab | All-in-one DevOps platform, built-in CI/CD, repo integration | Limited CD specialization, poor cross-project visibility, lacks reusable CD patterns |
| Azure DevOps | Microsoft ecosystem integration, CI/CD pipelines, artifacts | Project-centric view, limited hybrid/edge support, lacks blueprints and robust release governance |
| GitHub Actions | Event-driven CI/CD, GitHub integration, action library | Best for simple pipelines, lacks enterprise CD concepts, cross-environment tracking, and Day 2 ops |
| Jenkins | Open-source, plugin-rich, customizable automation | Script-heavy for CD, lacks native support for secure deployments, release promotion, governance, or scaling pipelines across environments |
Conclusion
Octopus Deploy stands out as a specialized, enterprise-ready platform for deployment automation and release management, offering capabilities that many general-purpose CI/CD tools or DIY solutions lack.
By focusing on complex delivery scenarios, multi-environment progression, Day 2 operations, and pipelines at scale, it provides organizations with the consistency, governance, and flexibility needed to manage modern and heritage applications across hybrid and distributed environments, while reducing operational risk and long-term maintenance overhead.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.

