What is Kubernetes CI/CD?
Kubernetes CI/CD refers to the integration of Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery practices within a Kubernetes ecosystem. CI/CD automates the process of software integration, testing, and deployment, accelerating development and ensuring reliable software releases.
In a Kubernetes environment, CI/CD automates the creation and management of containerized applications, enabling developers to deploy updates quickly and consistently across various environments. Implementing CI/CD in Kubernetes optimizes the software development lifecycle by providing a structured pipeline for code changes.
This process includes building containers, running automated tests, and deploying applications across clusters with minimal human intervention. By using Kubernetes’ orchestration capabilities, CI/CD improves scalability, maintains application reliability, and reduces the complexity of managing dynamic workloads.
Benefits of Kubernetes CI/CD for developers
Integrating CI/CD with Kubernetes brings significant advantages to development teams. Here are key benefits developers gain from using CI/CD in a Kubernetes environment:
- Faster release cycles: CI/CD pipelines automate repetitive tasks, reducing the time needed to test and deploy new code. This enables teams to release features and fixes more frequently.
- Consistent environments: Kubernetes provides a uniform environment for development, staging, and production. This minimizes environment-specific issues and helps ensure that applications behave the same way across all stages.
- Improved reliability and stability: Automated testing and deployment steps catch errors early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of bugs reaching production. Kubernetes’ self-healing features also help maintain uptime during deployments.
- Scalability by default: Kubernetes is built to scale applications horizontally. CI/CD processes can automatically adjust deployment strategies to meet traffic demands, improving system performance without manual intervention.
- Collaboration and transparency: CI/CD tools provide clear logs and dashboards. Combined with Kubernetes, this improves visibility into the deployment process, making it easier for teams to collaborate and troubleshoot issues.
- Simplified rollbacks: In case of deployment failures, CI/CD pipelines integrated with Kubernetes allow for quick and safe rollbacks.
Kubernetes CI/CD features for developers
When implementing CI/CD within Kubernetes, developers benefit from features tailored to the platform’s architecture and operational model:
- Declarative configuration: CI/CD tools in Kubernetes often adopt a declarative approach, where desired states are defined in version-controlled manifests. This allows teams to reproduce environments consistently, audit changes, and manage infrastructure as code.
- Native resource integration: CI/CD pipelines can natively interact with Kubernetes resources like deployments, services, and secrets. This enables precise control over application behavior and configuration directly within the cluster.
- Multi-environment support: Kubernetes-based CI/CD systems support environment-specific configurations, enabling isolated development, testing, and production environments within the same cluster or across multiple clusters. This separation reduces risk and improves test fidelity.
- GitOps workflows: GitOps—using Git as the source of truth—simplifies change tracking and rollback. CI/CD tools that support GitOps continuously reconcile the live cluster state with the state defined in Git, ensuring consistency and traceability.
- Custom resource support: Many platforms allow pipelines to interact with Kubernetes custom resource definitions (CRDs), enabling automation for operator-based applications or specialized workloads like databases or event-driven services.
- Progressive delivery capabilities: Kubernetes CI/CD supports advanced deployment strategies such as canary, blue/green, and rolling updates. These strategies reduce downtime and improve user experience by gradually introducing changes.
- Security and policy enforcement: Integrated CI/CD in Kubernetes can use RBAC, pod security policies, and admission controllers to enforce governance and access control, ensuring that only validated and authorized code reaches production.
- Observability and feedback loops: CI/CD pipelines integrated with Kubernetes provide detailed logs, metrics, and alerts through native and third-party observability tools. Developers receive real-time feedback on build status, test results, and deployment health.
Notable Kubernetes CI/CD tools for developers
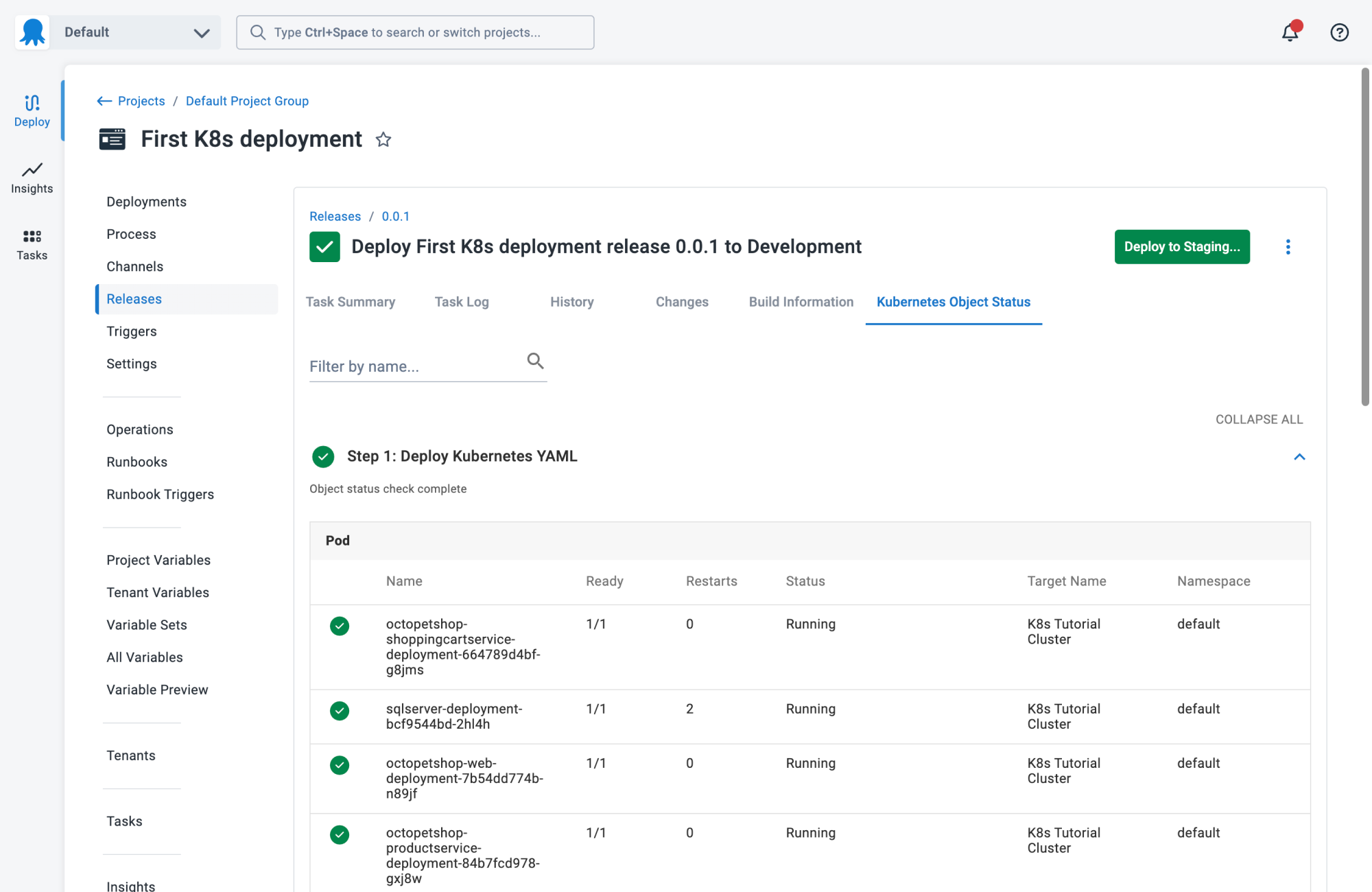
1. Octopus
Octopus makes it easy to deliver software to Kubernetes, multi-cloud, on-prem infrastructure, and anywhere else. It automates the release, deployment, and operations of your software and AI workloads.
General features of Octopus:
- Confident, risk-free deployments: Octopus gives you a consistent deployment process across all environments, so you can push to production with the same confidence and reliability as any other stage. Plus, with built-in rollback support, reverting to previous versions is always simple.
- Seamless scalability for deployments: Octopus is the only CD tool offering native multi-tenancy support. This means you can deploy to two, ten, or thousands of customers without ever duplicating your deployment process.
- Unified DevOps automation: Our runbooks automate routine and emergency operational tasks, freeing your teams to focus on more strategic work. They also enable other teams with safe, self-service operations.
- Compliance and security built in: With full auditing, role-based access control (RBAC), and single sign-on (SSO) built-in, Octopus simplifies compliance. This ensures accountability, peace of mind, and trust in all your deployments.
Kubernetes-specific features:
- Environment progression: Stop wasting time with tedious manifest file updates or custom scripts. Octopus’s built-in environment modeling and progression means you’ll spend less time on manual configurations and more time deploying.
- Single pane of glass: Get a complete, real-time overview of your deployments, all in one spot. Octopus gives you instant access to live status, deployment history, logs, and manifests across all your clusters and environments.
- Enterprise-grade compliance: Manage access to applications and environments with role-based access controls (RBAC). Plus, integrate with your existing ITSM tools for seamless change management.
2. Codefresh
Codefresh is a cloud-native CI/CD platform built specifically for Kubernetes environments. It provides a simplified, scalable solution for managing application delivery using modern practices like GitOps and progressive delivery. Designed around Argo, Codefresh unifies Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery in one platform.
General features
- Fast builds: Optimized build performance through caching and parallelization
- Progressive delivery: Support for canary and blue/green deployments to reduce deployment risk
- Automated rollbacks: Easily reverts to previous versions in case of deployment failures
- Pipeline reusability: DRY pipeline architecture using templates and inheritance to reduce duplication
- Lifecycle visibility: End-to-end observability from code commit to production
Kubernetes-specific features
- GitOps integration: Provides full GitOps support with Argo CD, allowing users to manage application states declaratively through Git repositories.
- Multi-cluster deployment: Helps deploy and manage applications across multiple Kubernetes clusters.
- Helm integration: Native support for Helm enables simplified packaging, versioning, and deployment of Kubernetes applications.
- Environment dashboards: Visualizes application status and promotion flow across environments (e.g., dev, staging, production) directly in the UI.
- Custom resource support: Manages Kubernetes custom resources (CRDs) within pipelines.
- Centralized management: A unified interface lets teams configure, monitor, and debug Kubernetes deployments centrally.
- Argo-powered automation: Uses Argo Workflows and Argo Rollouts to orchestrate complex workflows and progressive delivery strategies in Kubernetes.
![]()
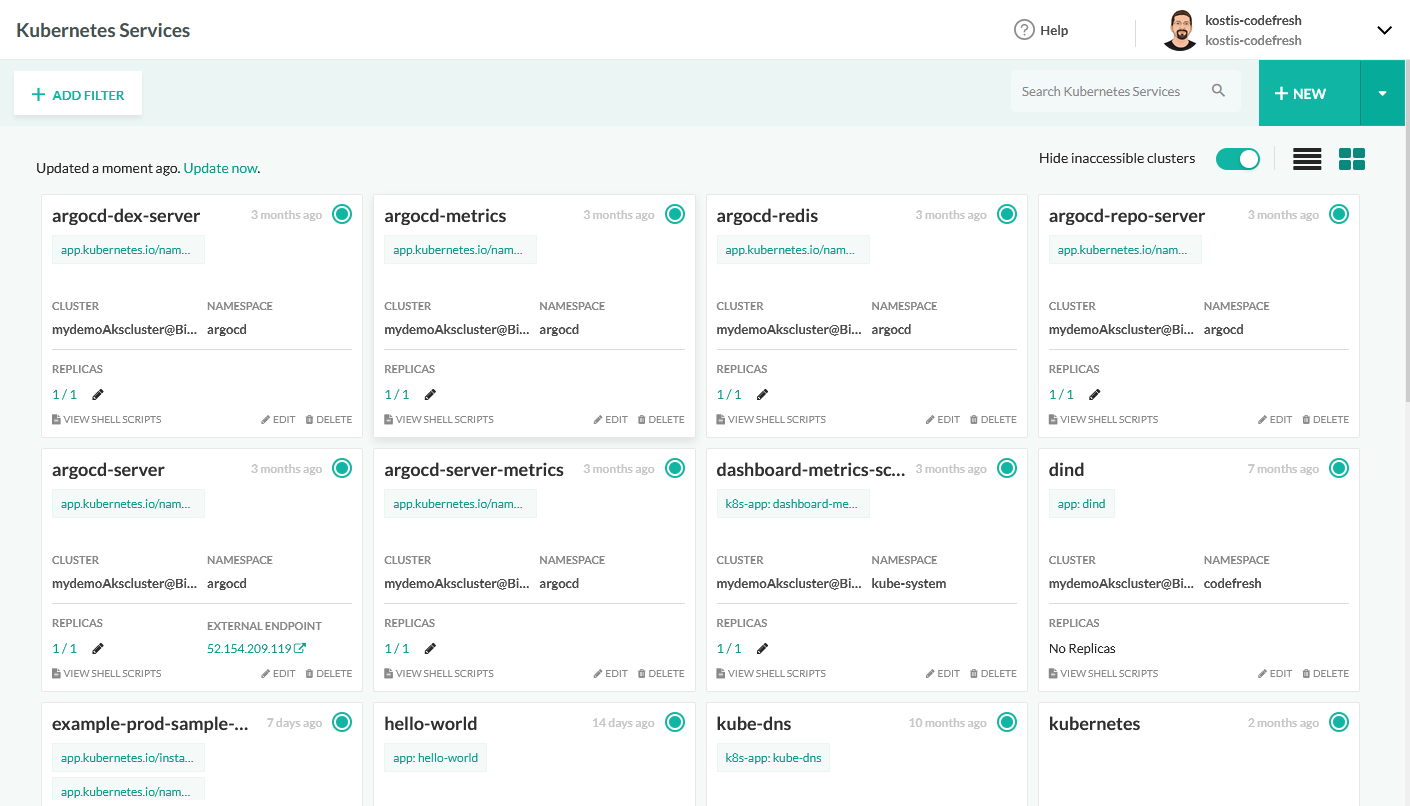
Source: Codefresh
3. GitLab CI/CD
GitLab CI/CD is a fully integrated Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery solution built into the GitLab platform. It automates the software delivery process, allowing teams to release secure applications faster.
General features
- End-to-end automation: Automates building, testing, packaging, and deploying code from a single platform
- Pipeline templates: Built-in or custom templates make it easier to create and manage CI/CD pipelines at scale
- Merge trains: Ensures clean, conflict-free merges by queuing and testing multiple merge requests in sequence
- Parent-child pipelines: Splits complex pipelines into smaller ones to reduce execution time and increase clarity
- Hosted runners: Provides managed infrastructure for running CI/CD jobs, or lets teams bring their own
Kubernetes-specific features
- GitLab Kubernetes Agent: Supports secure, two-way communication between GitLab and Kubernetes clusters for reliable CI/CD workflows.
- GitOps workflows: Supports pull-based deployment models, where GitLab detects changes in repositories and syncs them to Kubernetes using the agent.
- Cluster management: Allows teams to register, monitor, and interact with Kubernetes clusters directly from the GitLab UI.
- Multi-environment deployments: Enables deployment to different environments (e.g., dev, staging, prod) using environment-scoped configurations within pipelines.
- Secure, pull-based deployments: Ensures that deployment pipelines run from inside the cluster, reducing the attack surface and minimizing external dependencies.
- Real-time deployment tracking: Offers visibility into cluster state, application status, and deployment history through GitLab’s environment dashboards.
![]()
Source: GitLab
4. Argo CD
Argo CD is a declarative Continuous Delivery tool built for Kubernetes and designed around the GitOps methodology. It uses Git repositories as the single source of truth for managing application state and automates the deployment process by continuously syncing the desired state from Git to the live Kubernetes environment.
General features
- GitOps-based delivery: Uses Git as the source of truth for defining and deploying Kubernetes resources
- Multi-format support: Works with Helm, Kustomize, Jsonnet, plain YAML, and custom config plugins
- Automated synchronization: Continuously compares live and desired states and syncs changes automatically or manually
- Real-time monitoring: Visualizes application health and sync status through a web UI and CLI
- Cluster management: Supports deployment to multiple Kubernetes clusters from an Argo CD instance
Kubernetes-specific features
- Declarative application management: Manages applications entirely through Kubernetes manifests stored in Git, allowing reproducibility and version control.
- Namespace and cluster scoping: Supports application deployment within namespaces or across multiple clusters.
- Health and status checks: Continuously monitors the health and sync status of Kubernetes resources to detect drift and deployment issues.
- Resource diffing: Shows differences between the live state in the cluster and the desired state in Git, helping users understand what changes will be applied.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Enforces security policies within Kubernetes environments, restricting who can deploy, sync, or modify resources.
- Self-healing sync: Automatically restores the desired state in case of manual changes or failures in the live cluster.
- CRD support: Works with custom resource definitions (CRDs), enabling Kubernetes-native applications to be managed alongside core resources.
![]()
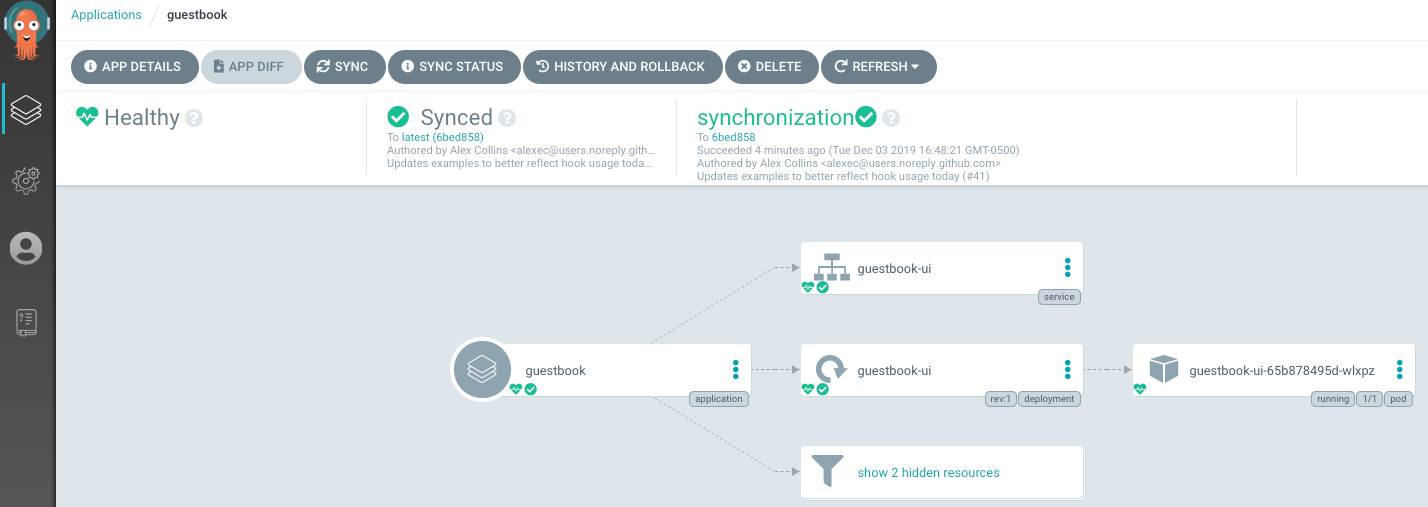
Source: Argo CD
5. Spinnaker
Spinnaker is an open-source, multi-cloud Continuous Delivery platform for releasing software changes across diverse cloud environments. Originally developed by Netflix, Spinnaker is purpose-built for managing complex application deployments, offering a pipeline management system and integrations with major cloud providers.
General features
- Multi-cloud deployments: Supports AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, Cloud Foundry, and Oracle Cloud
- Pipeline automation: Create pipelines that trigger from Git events, CI tools, or Docker image updates and automate testing, deployment, and monitoring
- Immutable infrastructure: Promotes reliable deployments with immutable image baking and deployment strategies like blue/green and canary
- Access control: Role-based access via OAuth, SAML, LDAP, Google Groups, and GitHub Teams
- Monitoring and notifications: Integrates with tools like Prometheus, Datadog, and New Relic for canary analysis and sends alerts via Slack, email, or SMS
Kubernetes-specific features
- Kubernetes-native deployments (v2 provider): Manages and deploys native Kubernetes objects (like deployments, services, config maps) directly, without needing baked manifests.
- Manifest-driven pipelines: Supports defining and deploying raw Kubernetes manifests from Git repositories, Helm charts, or Spinnaker’s UI.
- Multi-namespace support: Allows deploying to multiple namespaces and clusters, enabling environment-specific configurations and isolation.
- Artifact tracking: Tracks Kubernetes manifests and container images through the pipeline, ensuring accurate versioning and repeatability.
- Live manifest visibility: Provides a real-time view of Kubernetes resources deployed through Spinnaker, including rollout status and pod-level details.
- Integrated rollout strategies: Enables deployment strategies like blue/green, canary, and rolling updates, fully integrated into the Kubernetes workflow.
- Dynamic account and resource configuration: Supports dynamic account loading and lets users define custom Kubernetes kinds and resource versions.
![]()
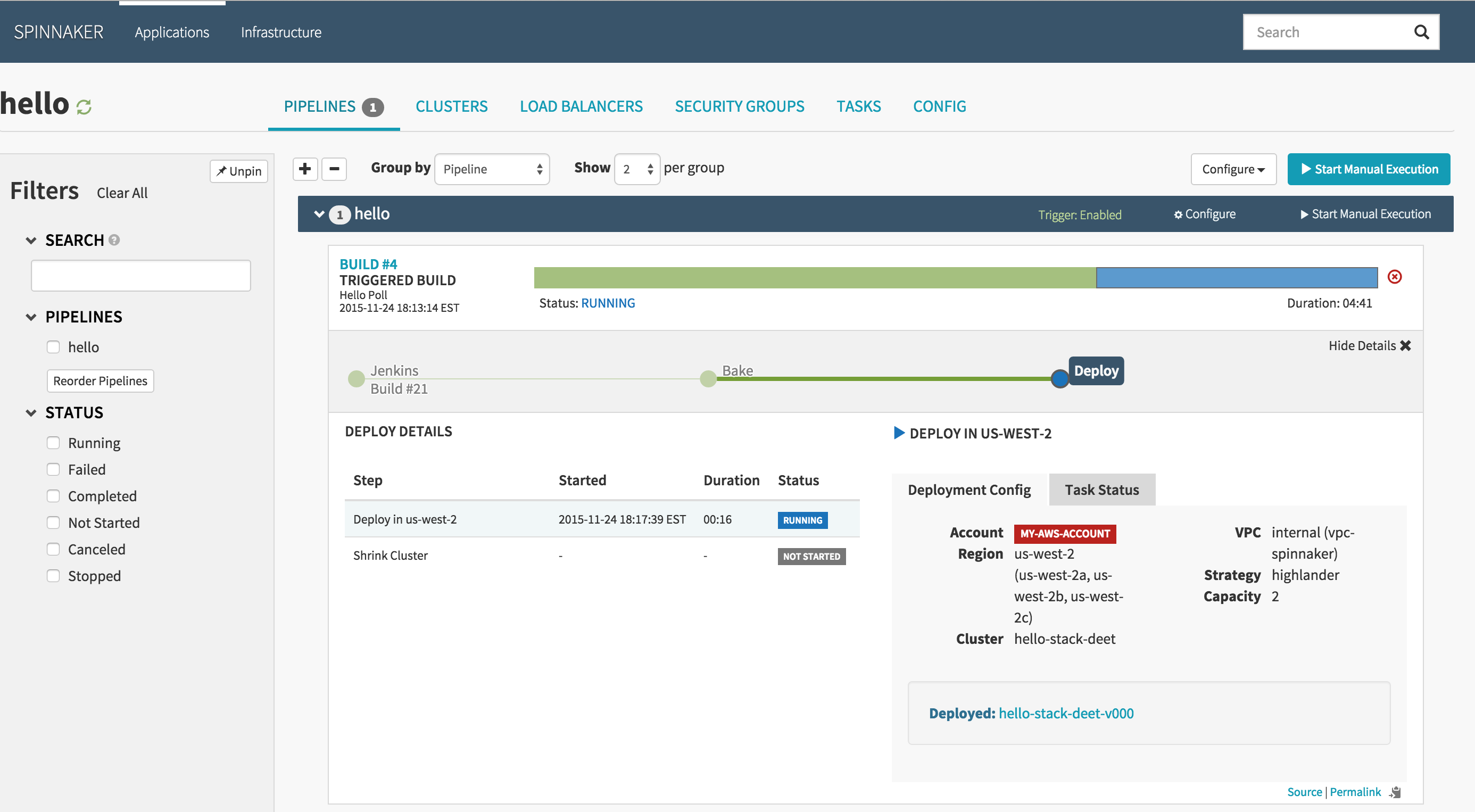
Source: Spinnaker
6. Tekton
Tekton is a cloud-native framework for creating CI/CD systems using Kubernetes-native resources. It allows platform engineers and developers to build and run custom pipelines using reusable building blocks called Tasks and Pipelines. As part of the Continuous Delivery Foundation, Tekton is open source and integrates into Kubernetes.
General features
- Kubernetes-native: Runs as an extension on a Kubernetes cluster using custom resources for pipelines and tasks.
- Composable pipelines: Uses Tasks and Pipelines as modular building blocks that can be reused and shared.
- Event-driven execution: Supports triggering pipelines automatically via Git events, pull requests, or webhooks using Tekton Triggers.
- Scalable by design: Scales horizontally with the Kubernetes cluster without pipeline reconfiguration.
- Standardized workflows: Uses the Kubernetes model to standardize how CI/CD is implemented across teams.
Kubernetes-specific features
- Custom resource definitions (CRDs): Defines pipelines, tasks, steps, and results as Kubernetes-native CRDs, making Tekton a natural extension of the Kubernetes API.
- Pod-based execution model: Each task step runs in its own container within Kubernetes pods, providing isolation and compatibility with Kubernetes scheduling and security policies.
- Tight cluster integration: Uses native Kubernetes features like namespaces, service accounts, and RBAC for secure, multi-tenant pipeline execution.
- Declarative configuration: Pipelines and tasks are fully declarative, aligning with Kubernetes best practices for version control and reproducibility.
- Native scaling and orchestration: Automatically benefits from Kubernetes autoscaling, load balancing, and fault tolerance without requiring external systems.
- Toolchain extensibility: Integrates smoothly with other Kubernetes-native tools (e.g., Argo CD, Knative) for end-to-end CI/CD workflows.
![]()
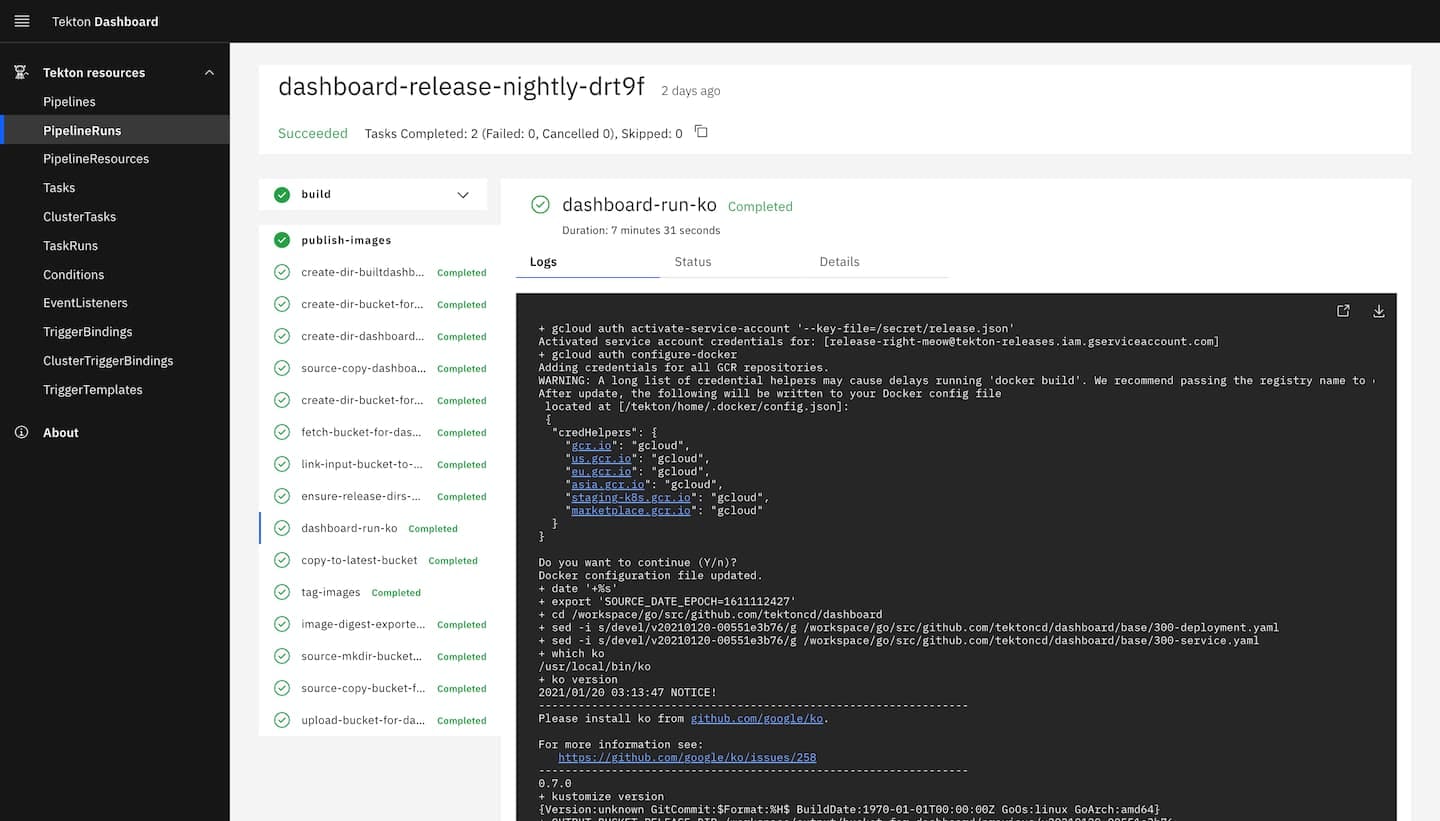
Source: Tekton
7. Buildkite
Buildkite is a CI/CD platform that enables engineering organizations to deliver software quickly through a modular set of tools, including pipeline orchestration, test optimization, artifact management, and mobile deployment infrastructure.
General features
- Scalable Pipeline orchestration: Buildkite Pipelines offer dynamic workflows with concurrency and runtime flexibility
- Test optimization: Buildkite Test Engine intelligently splits test suites, manages flaky tests, and improves test accountability
- Secure artifact management: Buildkite Package Registries provide fast, policy-controlled artifact storage with supply chain verification
- Mobile CI/CD: Buildkite Mobile Delivery Cloud accelerates mobile app builds using dedicated hardware and unified workflows
- Developer-centric feedback: Consolidated logs, real-time updates, and dynamic lifecycle hooks improve developer productivity
Kubernetes-specific features
- Cluster-based agent management: Buildkite’s Kubernetes integration allows teams to run Buildkite agents inside Kubernetes clusters for dynamic and scalable job execution.
- Pod-level isolation: Each job runs inside its own Kubernetes pod, ensuring isolation, better resource allocation, and easier debugging.
- Autoscaling agents: Kubernetes-based agents automatically scale up or down based on pipeline load, improving efficiency and cost control.
- Custom pod definitions: Teams can define job execution environments using custom Kubernetes pod specs to match specific workload requirements.
- Native Helm chart support: Provides official Helm charts for deploying and managing Buildkite agents within Kubernetes environments.
- Integrated secrets and config management: Uses Kubernetes-native secrets and config maps for secure and consistent configuration of CI/CD workflows.
![]()

Source: Buildkite
10. Harness
Harness is an AI-native software delivery platform that enables engineering teams to accelerate and secure the software lifecycle. It combines Continuous Integration, Delivery, feature management, security, and cost control into a unified platform.
General features
- AI-driven CI/CD: Automates and optimizes build, test, and deployment workflows using context-aware AI agents
- Multi-cloud CD & GitOps: Deploys across clouds, regions, and services with automated pipelines and GitOps support
- Feature flags & experimentation: Helps release and manage features with impact-driven experimentation and safe rollouts
- Infrastructure as code management: Automates IaC workflows with policy enforcement, cost tracking, and error reduction
- Chaos engineering: Users can inject controlled failures into pipelines to test application resilience with built-in experiments
Kubernetes-specific features
- Kubernetes service abstraction: Harness models applications as Kubernetes services, enabling consistent and reusable deployment configurations across environments.
- GitOps-driven deployments: Supports GitOps workflows by syncing desired states from Git to Kubernetes clusters using automated pipelines.
- Native support for Helm and Kustomize: Enables deployment and management of Kubernetes resources using Helm charts or Kustomize overlays.
- Dynamic provisioning: Automatically provisions namespaces, resources, and configurations during pipeline execution for ephemeral or multi-tenant environments.
- Multi-cluster and multi-environment support: Manages deployments across multiple clusters and environments with built-in controls and visibility.
- Integrated verification and rollback: Monitors Kubernetes deployment health post-release and automates rollback in case of failures using predefined thresholds and metrics.
- Secrets and config integration: Works with Kubernetes secrets and external secret managers for secure configuration management within pipelines.
![]()
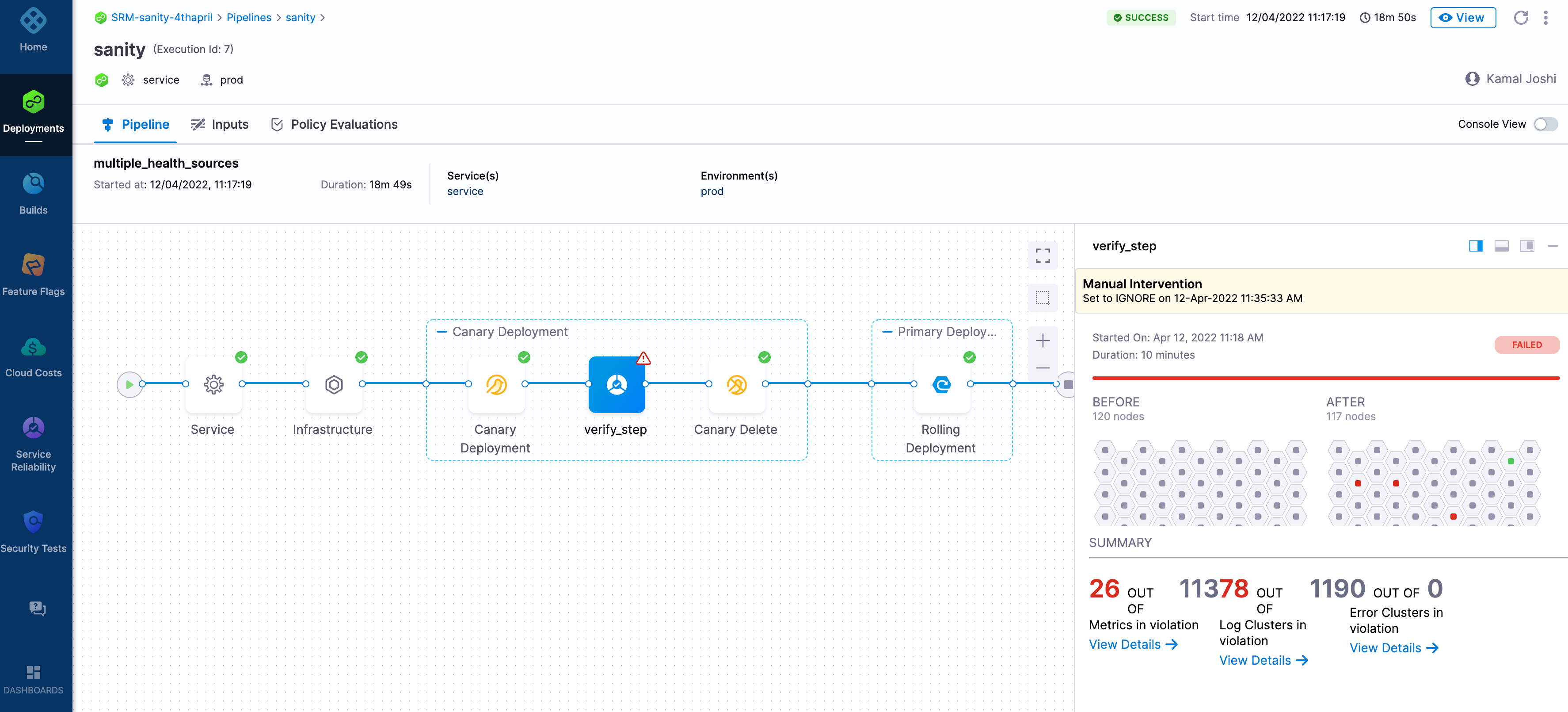
Source: Harness
Conclusion
Integrating CI/CD into Kubernetes environments enables teams to deliver software with greater speed, reliability, and control. By automating every stage of the delivery pipeline—from code commits to production rollouts—development becomes more iterative, scalable, and resilient. This approach minimizes manual errors, shortens feedback loops, and supports continuous improvement.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.