What is blue/green deployment?
Blue/green deployment is a strategy for software deployments that minimizes downtime and risks by running two identical production environments. The “blue” environment represents the current live instance, while the “green” environment is the testing ground for new releases.
When the new release in the green environment is stable and tested, traffic is switched from the blue to the green environment, making the green environment live. This switch allows a fast rollback if issues arise, as traffic can be routed back to the blue environment. The primary goal of blue/green deployment is to deliver updates without service interruptions.
This method also ensures that the previous version is always readily available, reducing the risk of deployment failure. Developers can work on updates in isolation in the green environment without affecting the current live services.
This is part of a series of articles about CI/CD
How do CI/CD tools enable blue/green deployments?
CI/CD tools enable blue/green deployments by automating the processes required to create, manage, and switch between the two environments. These tools integrate deployment automation, traffic routing, and monitoring, ensuring seamless and controlled transition from blue to green environments.
Most CI/CD platforms offer pipeline templates and plugins that handle infrastructure provisioning, deployment steps, and health checks. These tools coordinate deployments with load balancers, service meshes, or DNS updates to reroute traffic safely.
By incorporating automated rollbacks and monitoring hooks, CI/CD tools help teams quickly detect issues and revert to the stable environment without manual intervention. Additionally, integration with infrastructure-as-code (IaC) frameworks allows teams to maintain environment consistency, ensuring blue and green environments remain identical throughout the deployment cycle.
Benefits of blue/green deployment for CI/CD
Blue/green deployment aids in Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) by ensuring smooth and reliable software releases:
- Minimal downtime: Since traffic is switched instantly between environments, users experience little to no downtime during deployments.
- Quick rollbacks: If an issue is detected after deployment, traffic can be redirected back to the previous version.
- Safer releases: The new version is thoroughly tested in the green environment before going live, reducing the risk of introducing bugs into production.
- Continuous Delivery support: Blue/green deployment enables frequent updates, aligning with CI/CD practices for faster software delivery.
- No impact on active users: Updates and testing happen in isolation, ensuring users are not affected by development or deployment activities.
- Consistent testing environment: Since the green environment mirrors production, testing conditions are identical, improving reliability and accuracy.
- Simplified troubleshooting: Issues can be diagnosed without affecting the live system, allowing for smoother debugging and resolution.
Notable CI/CD tools supporting blue/green deployment
1. Octopus
Octopus Deploy is a sophisticated, best-of-breed Continuous Delivery (CD) platform for modern software teams. It offers powerful release orchestration, deployment automation, and runbook automation while handling the scale, complexity, and governance expectations of even the largest organizations with the most complex deployment challenges.
General features:
- Define your deployment process once and use it across all environments so you can deploy to production with the same confidence you deploy everywhere else.
- Octopus is the only CD tool with built-in multi-tenancy support. You can deploy many customer-specific instances using the same deployment process.
- You can use runbooks to automate operations tasks to remove toil. You can use runbooks to provide safe self-service operations to other teams.
- Octopus has role-based access control, single-sign-on (SSO) as standard, and a complete audit trail to make audits a breeze.
Blue/green deployment features:
- Built-in support for modeling blue/green deployments as environments
- Multi-environment phases allow new versions to be sent to either the blue or green environment
- Visibility into which version is deployed for the blue environment and green environment
- Snapshots ensure the packages and deployment process are applied consistently to each environment
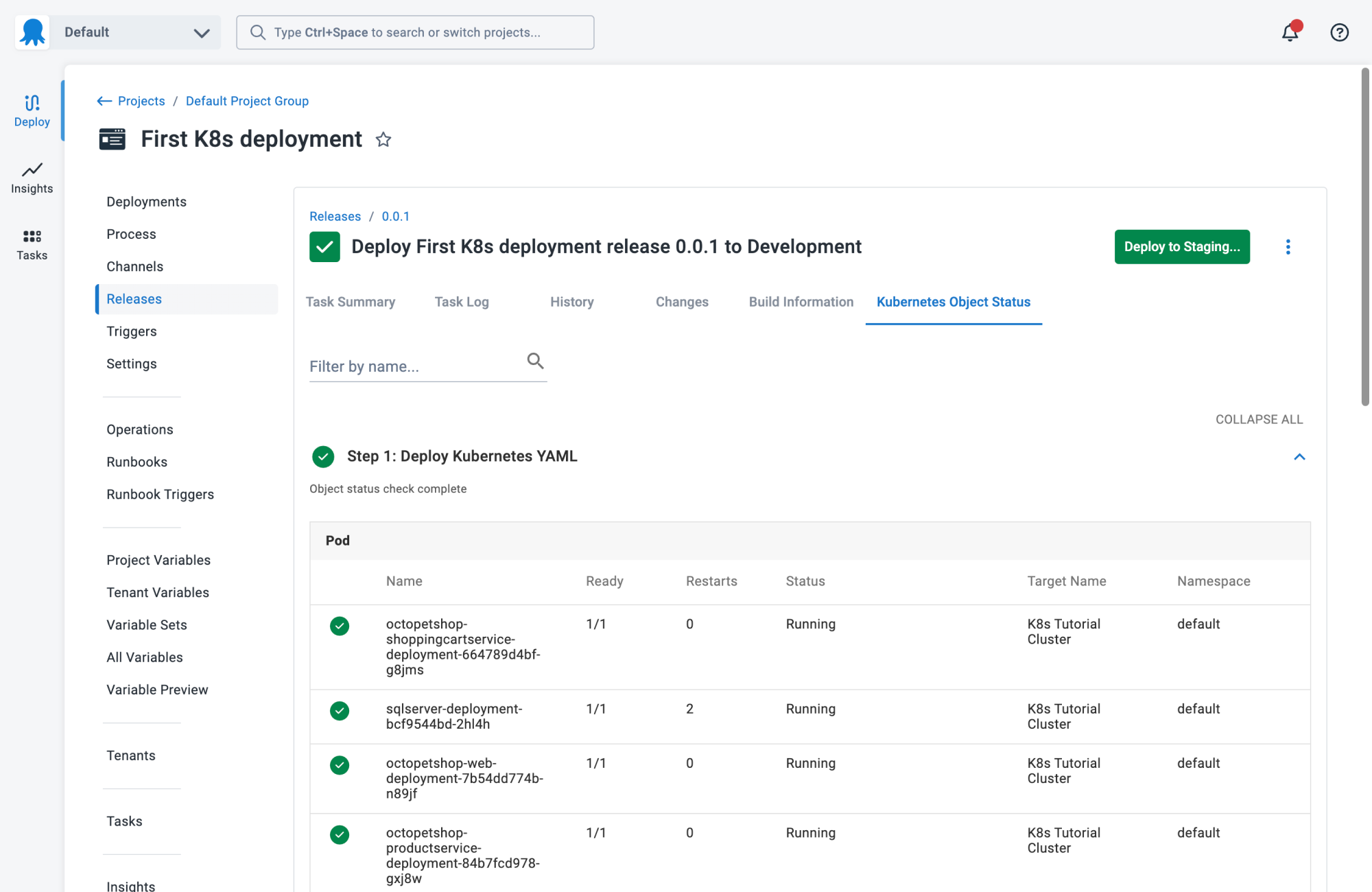
2. Codefresh
Codefresh is a CI/CD platform built for cloud-native applications, with a focus on Kubernetes and GitOps-based deployments. It emphasizes rapid build, test, and deployment cycles using containerized environments. Codefresh provides visual pipelines, integrated GitOps capabilities, and supports multi-cloud deployments.
General features:
- Kubernetes-native pipelines: Offers YAML and visual editors for building cloud-native pipelines.
- Integrated GitOps: Works with Argo CD to manage GitOps workflows.
- Debugging: Provides real-time dashboards, logs, and side-by-side events.
- Built-in registry and Helm support: Supports Docker and Helm for packaging and deployment.
- Progressive delivery support: Natively supports blue/green, canary, and A/B deployments.
Blue/green deployment features:
- Automated traffic switching: Manages routing using Kubernetes ingress controllers or service meshes.
- Instant rollbacks: Enables automatic rollbacks on failure based on health checks.
- Deployment visibility: Displays environment states and history to monitor deployment health.
- Pipeline templates: Includes ready-made templates for blue/green strategies.
- Routing updates: Integrates with service mesh or ingress for traffic control.
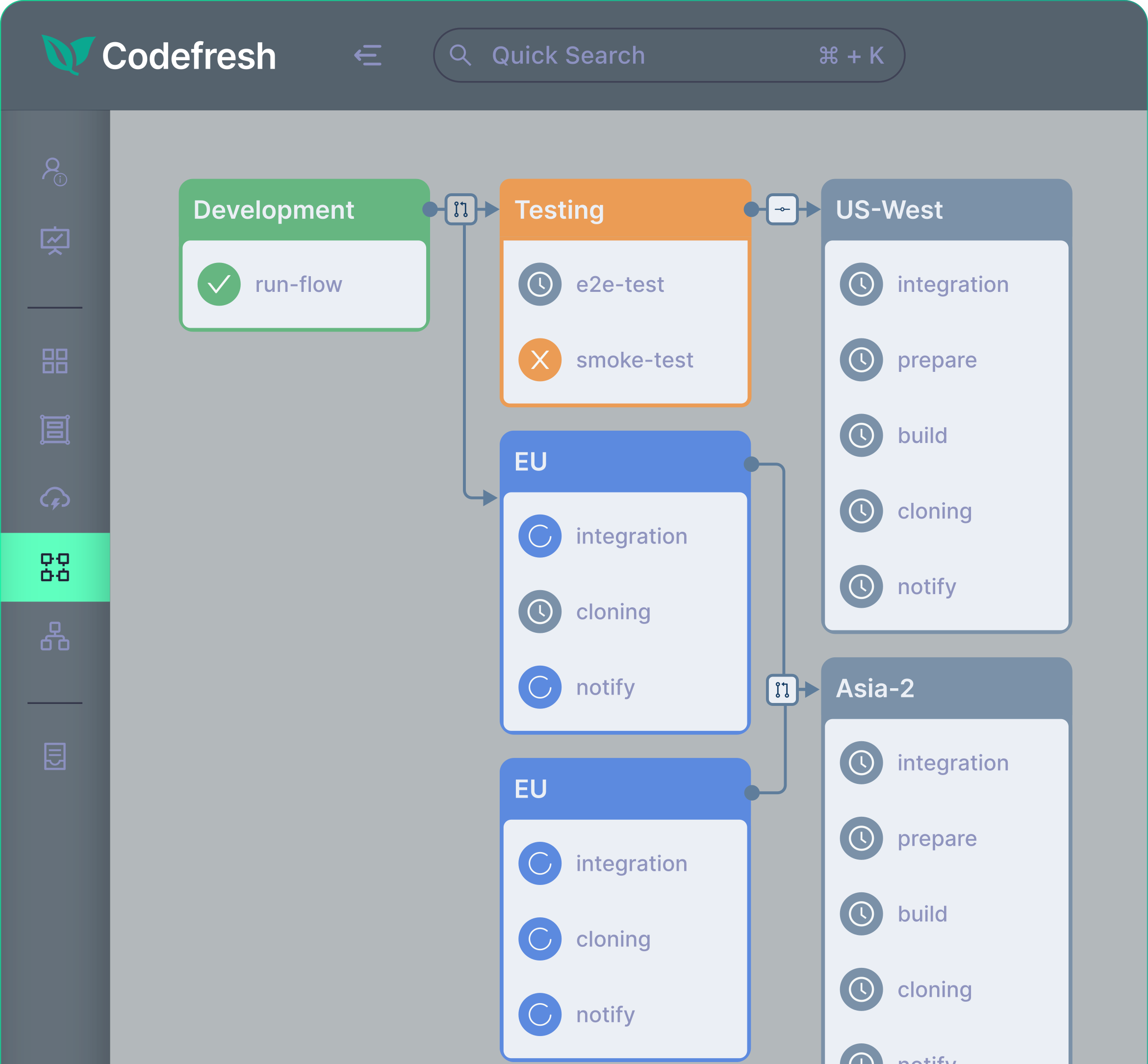
3. AWS CodeDeploy
AWS CodeDeploy is a fully managed deployment service that automates software releases to various compute services, including Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, Amazon ECS, and on-premises servers. It supports multiple deployment strategies, such as in-place, canary, linear, and blue/green deployments.
General features:
- Multi-environment support: Supports EC2, Lambda, ECS, and on-premises servers.
- Automated rollback: Detects failures and triggers automatic rollback.
- Integrated AWS ecosystem: Works with CloudWatch, CodePipeline, and CloudFormation.
- Deployment hooks: Allows custom pre- and post-deployment scripting.
- Traffic shifting strategies: Supports linear, canary, and blue/green strategies.
Blue/green deployment features:
- Automated traffic switching: Uses load balancers to shift traffic between environments.
- Instant rollbacks: Rolls back deployments automatically on health check failures.
- Deployment visibility: Offers logs and metrics through AWS CloudWatch.
- DNS integration: Works with Route 53 for DNS-based traffic management.
- Health validation: Validates new versions before routing full production traffic
- Blue/green deployments for EC2 and ECS: Provisions replacement instances or container task sets, ensuring a smooth transition between application versions.
![]()
Source: AWS CodeDeploy
4. Azure Container Apps
Azure Container Apps is a serverless container platform that simplifies the deployment and management of cloud-native applications. It allows developers to run microservices, APIs, and background jobs without handling infrastructure complexities. The platform supports dynamic scaling based on HTTP traffic, CPU/memory usage, and event-driven processing.
General features:
- Serverless container hosting: Supports scaling based on HTTP traffic, CPU, or memory.
- Event-driven processing: Integrates with Azure Functions and Logic Apps for event handling.
- Secure networking: Supports VNET integration and Dapr for secure service discovery.
- Integrated observability: Uses Azure Monitor and Log Analytics for observability.
- Revision management: Supports multiple revisions for controlled deployments.
Blue/green deployment features:
- Traffic splitting: Supports blue/green deployments by enabling controlled traffic distribution across application versions.
- Instant rollbacks: Supports traffic shifting back to previous revisions without redeploying.
- Deployment visibility: Monitors revision health and traffic patterns during deployments.
- Fine-grained control: Allows per-revision traffic allocation.
- Integrated observability: Offers metrics and logs to monitor deployment status.
- Multiple revisions management: Runs multiple container revisions simultaneously, making it easier to test new versions before fully switching traffic.
![]()
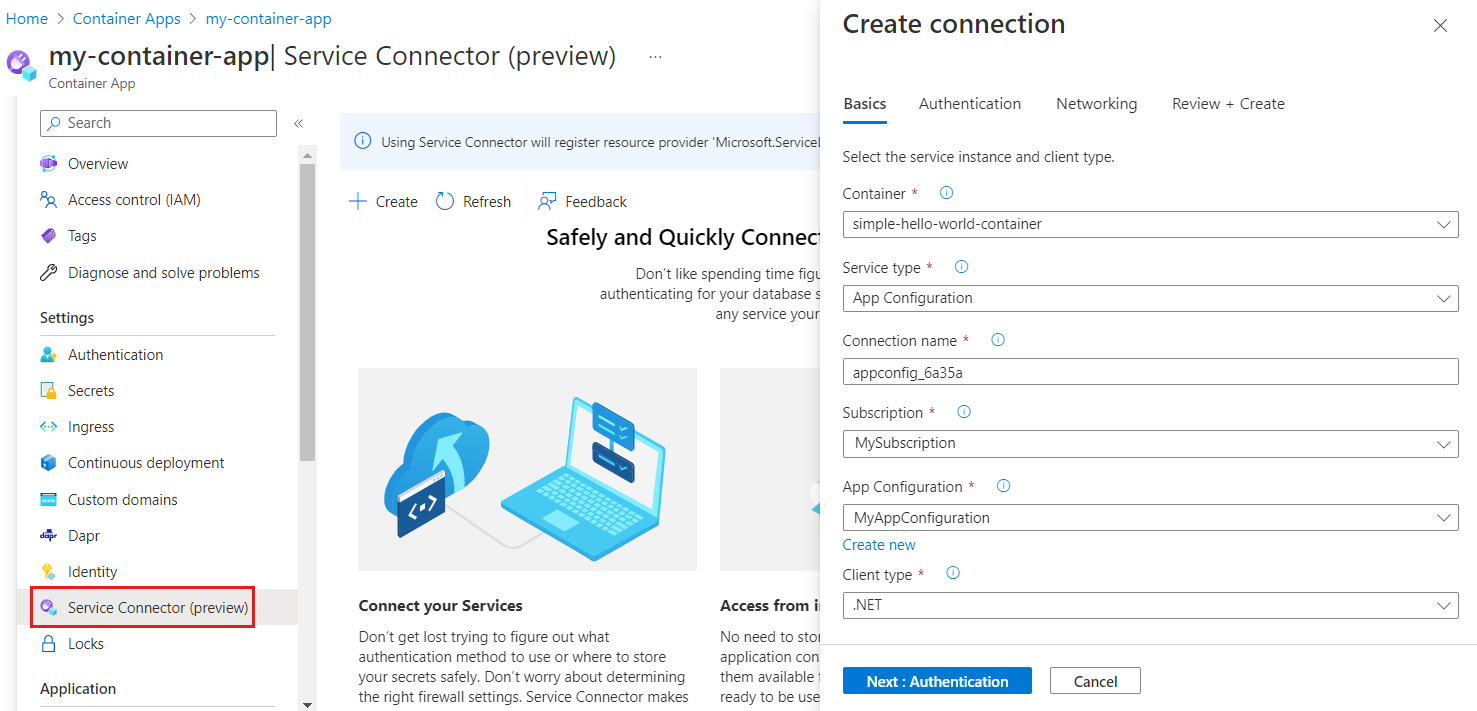
Source: Microsoft
5. Google Cloud Deployment Manager
Google Cloud Deployment Manager is an infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tool that automates the provisioning and management of Google Cloud resources. It allows users to define infrastructure configurations using YAML, Jinja2, or Python templates, ensuring consistency and repeatability across deployments.
General features:
- Infrastructure as code: Supports reusable YAML, Jinja2, and Python templates for IaC.
- Automated resource management: Manages Google Cloud resources declaratively.
- Version-controlled deployments: Enables repeatable, consistent deployments.
- Integrated observability: Works with Google Cloud Monitoring and Logging.
- API extensibility: Supports custom deployments via APIs and templates.
Blue/green deployment features:
- Automated traffic switching: Supports traffic shifting using Google Cloud Load Balancing.
- Instant rollbacks: Allows rollback by reverting to previous template versions.
- Deployment visibility: Integrates with Cloud Monitoring to track health and logs.
- Parallel environment provisioning: Provisions blue and green environments simultaneously.
- Traffic management with GKE: Works with Kubernetes Engine and service meshes for traffic control.
![]()
Source: Google Cloud
Best practices for implementing blue/green deployment in CI/CD pipelines
Here are some considerations to ensure effective blue/green deployment when working with CI/CD pipelines.
1. Implement infrastructure as code (IaC)
To ensure consistency between blue and green environments, it is essential to manage infrastructure through IaC tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Google Cloud Deployment Manager. IaC allows developers to define the entire environment configuration—including networking, security, and compute resources—in code.
This guarantees that both environments are exact replicas, minimizing configuration drift and deployment surprises. By versioning the infrastructure code alongside application code, teams can track changes, roll back to previous configurations, and maintain an auditable change history. Automating environment provisioning through IaC accelerates the setup of blue/green deployments.
2. Conduct comprehensive testing in the green environment
Thorough testing in the green environment is crucial to ensure the stability and performance of new releases before they go live. This approach involves conducting a full suite of tests, including unit, integration, and acceptance testing, within the green environment, which mirrors the production setting.
Automated testing tools enable thorough testing processes, allowing rapid iteration and feedback. Conducting these tests in a production-like environment ensures that edge cases are identified and addressed, reducing the risk of post-deployment issues.
3. Use feature flags
Feature flags aid in implementing blue/green deployment, offering granular control over feature rollouts. By decoupling feature deployment from code releases, feature flags allow teams to toggle functionality on or off without redeploying the code. This flexibility enables gradual feature rollouts, testing in production environments, and quick rollbacks if necessary.
Many tools offer feature flagging capabilities that integrate with CI/CD pipelines. These tools provide developers with the ability to conduct A/B testing and canary releases, helping them gather user feedback and measure the impact of new features in real time.
4. Ensure network and security parity
Both environments should maintain the same security configurations and network settings to prevent unexpected behavior during the transition. This involves synchronizing firewalls, access controls, and other critical security measures across environments. Automation tools can help enforce consistent security policies.
By maintaining parity, organizations protect against security vulnerabilities that could arise during deployment transitions. It guarantees that both environments are subjected to the same security scrutiny, minimizing the risk of breaches resulting from configuration disparities. Consistent networking settings also ensure that the application performs identically in both environments.
Conclusion
Blue/green deployment is a proven strategy for reducing deployment risks, minimizing downtime, and enabling safer, more controlled software releases. By maintaining two identical environments and automating the transition between them, teams can ensure that updates are thoroughly tested and validated before impacting users. This approach improves the stability and reliability of software delivery pipelines and supports the goals of CI/CD practices.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.